Axl and Mertk Receptors Cooperate to Promote Breast Cancer Progression by Combined Oncogenic Signaling and Evasion of Host Antitumor Immunity
- PMID: 33239426
- PMCID: PMC9999365
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2066
Axl and Mertk Receptors Cooperate to Promote Breast Cancer Progression by Combined Oncogenic Signaling and Evasion of Host Antitumor Immunity
Abstract
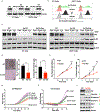
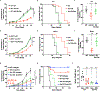
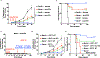
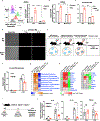
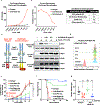
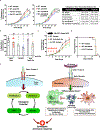
Despite the promising clinical benefit of targeted and immune checkpoint blocking therapeutics, current strategies have limited success in breast cancer, indicating that additional inhibitory pathways are required to complement existing therapeutics. TAM receptors (Tyro-3, Axl, and Mertk) are often correlated with poor prognosis because of their capacities to sustain an immunosuppressive environment. Here, we ablate Axl on tumor cells using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing, and by targeting Mertk in the tumor microenvironment (TME), we observed distinct functions of TAM as oncogenic kinases, as well as inhibitory immune receptors. Depletion of Axl suppressed cell intrinsic oncogenic properties, decreased tumor growth, reduced the incidence of lung metastasis and increased overall survival of mice when injected into mammary fat pad of syngeneic mice, and demonstrated synergy when combined with anti-PD-1 therapy. Blockade of Mertk function on macrophages decreased efferocytosis, altered the cytokine milieu, and resulted in suppressed macrophage gene expression patterns. Mertk-knockout mice or treatment with anti-Mertk-neutralizing mAb also altered the cellular immune profile, resulting in a more inflamed tumor environment with enhanced T-cell infiltration into tumors and T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity. The antitumor activity from Mertk inhibition was abrogated by depletion of cytotoxic CD8α T cells by using anti-CD8α mAb or by transplantation of tumor cells into B6.CB17-Prkdc SCID mice. Our data indicate that targeting Axl expressed on tumor cells and Mertk in the TME is predicted to have a combinatorial benefit to enhance current immunotherapies and that Axl and Mertk have distinct functional activities that impair host antitumor response. SIGNIFICANCE: This study demonstrates how TAM receptors act both as oncogenic tyrosine kinases and as receptors that mediate immune evasion in cancer progression.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tumor-initiating cells escape tumor immunity via CCL8 from tumor-associated macrophages in mice.J Clin Invest. 2025 Jan 7;135(5):e180893. doi: 10.1172/JCI180893. J Clin Invest. 2025. PMID: 39774471 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of lung homeostasis and silicosis by the TAM receptors MerTk and Axl.Front Immunol. 2024 May 7;15:1380628. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1380628. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38774866 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylserine Sensing by TAM Receptors Regulates AKT-Dependent Chemoresistance and PD-L1 Expression.Mol Cancer Res. 2017 Jun;15(6):753-764. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-16-0350. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Mol Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28184013 Free PMC article.
-
TAM receptor tyrosine kinases as emerging targets of innate immune checkpoint blockade for cancer therapy.Immunol Rev. 2017 Mar;276(1):165-177. doi: 10.1111/imr.12522. Immunol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28258690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TAM-ing T cells in the tumor microenvironment: implications for TAM receptor targeting.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020 Feb;69(2):237-244. doi: 10.1007/s00262-019-02421-w. Epub 2019 Oct 29. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020. PMID: 31664482 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
STAMBPL1/TRIM21 Balances AXL Stability Impacting Mesenchymal Phenotype and Immune Response in KIRC.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jan;12(1):e2405083. doi: 10.1002/advs.202405083. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39527690 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Control of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by TAM Receptors.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 29;13(21):5448. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215448. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Axl inhibitor-mediated reprogramming of the myeloid compartment of the in vitro tumor microenvironment is influenced by prior targeted therapy treatment.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 5;16:1601420. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1601420. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40539073 Free PMC article.
-
Axl Regulation of NK Cell Activity Creates an Immunosuppressive Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Head and Neck Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 15;17(6):994. doi: 10.3390/cancers17060994. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149328 Free PMC article.
-
MerTK+ macrophages promote melanoma progression and immunotherapy resistance through AhR-ALKAL1 activation.Sci Adv. 2024 Oct 4;10(40):eado8366. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ado8366. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39365866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng X, Li L, Thorpe PE, Yopp AC, Brekken RA, Huang X. Antibody-Mediated Blockade of Phosphatidylserine Enhances the Antitumor Effect of Sorafenib in Hepatocellular Carcinomas Xenografts. Ann Surg Oncol 2016;23:583–91 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

