Facing the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Role of Sense of Coherence
- PMID: 33240166
- PMCID: PMC7677188
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.578440
Facing the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Role of Sense of Coherence
Abstract
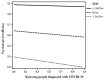
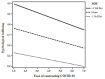
The worldwide outbreak of COVID-19, the ensuing pandemic, and the related containment measures pose considerable challenges to psychological resilience and well-being. Researchers are now forced to look for resources to cope with negative experiences linked to this health emergency. According to the salutogenic approach proposed by Antonovsky, the sense of coherence (SOC) is a major source of resilience. Thus, this study aimed at assessing the role of SOC in moderating the link between illness experiences (in terms of knowing persons diagnosed with COVID-19 and fear of contracting COVID-19) and psychological well-being. 2,784 participants, taken from a large sample of the Italian population (65.4% females) and aged between 18 and 85 years, filled in an anonymous online survey during the 3rd week of the lockdown. Findings supported the moderating role of SOC in shaping the link between illness experiences and psychological well-being. Specifically, participants who knew at least one person diagnosed with COVID-19 showed lower levels of psychological well-being at low levels of SOC. The negative relation between participants' fear of contracting COVID-19 and psychological well-being was stronger for those who showed higher levels of SOC. This study discusses the implications of these results for interventions aimed at reducing the pandemic's detrimental effects and promoting resilience.
Keywords: COVID-19; fear; illness; sense of coherence; well-being.
Copyright © 2020 Barni, Danioni, Canzi, Ferrari, Ranieri, Lanz, Iafrate, Regalia and Rosnati.
Figures
References
-
- Aiken L. S., West S. G. (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
-
- Antonovsky A. (1979). Health, stress, and coping. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
-
- Antonovsky A. (1987). Unravelling mystery of health: How people manage stress and stay well. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
-
- Antonovsky A. (1996). The salutogenic model as a theory to guide health promotion. Health Promot. Int. 11, 11–18. 10.1093/heapro/11.1.11 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

