Association between IDO activity and prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer after radiotherapy
- PMID: 33241018
- PMCID: PMC7576049
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-5634
Association between IDO activity and prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer after radiotherapy
Abstract
Background: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), a limiting enzyme in the IDO/kynurenine (Kyn) pathway, converts tryptophan (Trp) into Kyn, and plays a significant role in immune suppression and tumor immune evasion. This study aimed to investigate the association between IDO activity and clinical outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients who underwent radiotherapy (RT).
Methods: Serum Kyn and Trp levels were measured in 104 NSCLC patients by high-performance liquid chromatography at baseline, and the following RT. The correlation between IDO activity, as computed by Kyn: Trp ratios and survival was estimated using Kaplan-Meier curves. Cox proportional hazard models are used in the univariate and multivariate analyses.
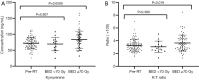
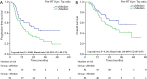
Results: Both the Kyn levels and Kyn:Trp ratios were reduced after RT at a biologically equivalent dose (BED) of <70 Gy, while these increased at a BED of ≥70 Gy. Post/pre-Kyn levels were positively correlated with an objective response. Patients with a higher Kyn:Trp ratio pre-RT had the worse median progression-free survival (mPFS, 13.5 vs. 24.5 months, P=0.049). Higher post/pre-Kyn:Trp ratios were correlated with improved median overall survival (mOS, 23.8 months vs. not reached, P=0.032). On the multivariate analysis, pre-RT Kyn:Trp and post/pre-Kyn:Trp ratios remained as independent predictive factors for PFS and OS, respectively.
Conclusions: It was proved that RT could alter IDO-mediated immune activity and establish strong correlations between IDO activity and survival outcomes in NSCLC patients treated with RT. These present findings suggest that the profiling of IDO activity might allow for the prompt adjustment of RT doses and better predict patient response to RT.
Keywords: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity (IDO activity); non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); prognosis; radiotherapy-induced immune response.
2020 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-5634). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamic change of IDO1 activity predicts survival in patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC and chemoradiotherapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 10;13:906815. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.906815. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36032151 Free PMC article.
-
Can IDO activity predict primary resistance to anti-PD-1 treatment in NSCLC?J Transl Med. 2018 Aug 6;16(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1595-3. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30081936 Free PMC article.
-
Tryptophan Catabolism as Immune Mechanism of Primary Resistance to Anti-PD-1.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 7;11:1243. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01243. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32733441 Free PMC article.
-
Immune modulations during chemoimmunotherapy & novel vaccine strategies--in metastatic melanoma and non small-cell lung cancer.Dan Med J. 2013 Dec;60(12):B4774. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 24355457 Review.
-
Redox reactions related to indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and tryptophan metabolism along the kynurenine pathway.Redox Rep. 1999;4(5):199-220. doi: 10.1179/135100099101534927. Redox Rep. 1999. PMID: 10731095 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Diversities of Regulatory T Cells in the Context of Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 17;13:833667. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.833667. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35371055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tobacco carcinogen induces tryptophan metabolism and immune suppression via induction of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Sep 7;7(1):311. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01127-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36068203 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Lung Cancer: Insights and Perspectives.Pathogens. 2022 Jan 21;11(2):132. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11020132. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35215076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic change of IDO1 activity predicts survival in patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC and chemoradiotherapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 10;13:906815. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.906815. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36032151 Free PMC article.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Immune Status as a Potential Biomarker of Radioiodine Efficacy for Advanced Distant Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 18;12:871792. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.871792. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35924153 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
