Burden of Disease in PWH Harboring a Multidrug-Resistant Virus: Data From the PRESTIGIO Registry
- PMID: 33241063
- PMCID: PMC7673611
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa456
Burden of Disease in PWH Harboring a Multidrug-Resistant Virus: Data From the PRESTIGIO Registry
Abstract
Background: Currently, no data are available on the burden of morbidity and mortality in people with HIV-1 (PWH) harboring a 4-class drug-resistant (4DR) virus (nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, protease inhibitors, integrase strand transfer inhibitors). The study aimed to assess the incidence of clinical events and death in this population.
Methods: This was a cohort study on PWH from the PRESTIGIO Registry with a documented 4DR virus. Burden of disease was defined as the occurrence of any new event including an AIDS-defining event (ADE) or non-AIDS-defining event (NADE) or death from any cause after 4DR evidence (baseline). Cox regression models evaluated factors associated with the risk of new clinical events/death.
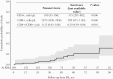
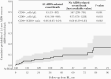
Results: Among 148 PWH followed for a median (interquartile range) of 47 (32-84) months after 4DR evidence, 38 PWH had 62 new events or died from any cause (incidence rate, 9.12/100 person-years of follow-up; 95% CI = 6.85-11.39): 12 deaths (6 AIDS-related and 6 non-AIDS-related), 18 ADEs, 32 NADEs; 20 of the 38 NADEs (45%) of the incident clinical events were malignancies. The 4-year cumulative incidence of death was 6% (95% CI, 3%-13%), and that of ≥1 event or death was 22% (95% CI, 16%-31%). A higher risk of new clinical events/death was more likely in PWH with previous clinical events (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.67; 95% CI, 1.07-6.67) and marginally associated with lower baseline CD4+/CD8+ ratio (aHR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.65-1.02).
Conclusions: PWH harboring 4DR have a high burden of disease with a worrying incidence of malignancies, strongly advising for close prevention and monitoring interventions as well as access to innovative therapeutic strategies, especially in people with a history of clinical events and low CD4+/CD8+ ratio.
Keywords: 4-class drug resistance; AIDS-defining event; cancer; death; non-AIDS-defining event.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- Raffi F, Esser S, Nunnari G, et al. Switching regimens in virologically suppressed HIV-1-infected patients: evidence base and rationale for integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI)-containing regimens. HIV Med 2016; 17(Suppl 5):3–16. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa F, Lodwick R, Costagliola D, et al. Calendar time trends in the incidence and prevalence of triple-class virologic failure in antiretroviral drug-experienced people with HIV in Europe. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2012; 59:294–9. - PubMed
-
- Lombardi F, Giacomelli A, Armenia D, et al. Evaluation of multidrug resistance over the last two decades in art-experienced HIV-1 infected patients in the ARCA database. Paper presented at: Italian Conference on AIDS and Antiviral Research (ICAR); 5–7 June, 2019; Milan, Italy.
-
- Zaccarelli M, Tozzi V, Lorenzini P, et al. ; Collaborative Group for Clinical Use of HIV Genotype Resistance Test (GRT) at National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani Multiple drug class-wide resistance associated with poorer survival after treatment failure in a cohort of HIV-infected patients. AIDS 2005; 19:1081–9. - PubMed

