Dataset of sodium chloride sterile liquid in bottles for intravenous administration and fill level monitoring
- PMID: 33241092
- PMCID: PMC7672290
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2020.106472
Dataset of sodium chloride sterile liquid in bottles for intravenous administration and fill level monitoring
Abstract
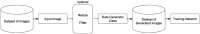
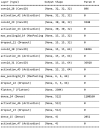
We propose a dataset to investigate the relationship between the fill level of bottles and tiny machine learning algorithms. Tiny machine learning is represented by any Artificial Intelligence algorithm (spanning from conventional decision tree classifiers to artificial neural networks) that can be deployed into a resource constrained micro controller unit (MCU). The data presented has been originally collected for a joint research project by STMicroelectronics and Sesovera.ai. This article describes the recorded image data of bottles with 4 levels of filling. The bottles contain sodium chloride sterile liquid for intravenous administration. One subject of investigation using this dataset could be the classification of the liquid fill level, for example, to ease continuous human visual monitoring which may represent an onerous time-consuming task. Automating the task can help to increase the human work productivity thus saving time. Under normal circumstances, human visual monitoring of the saline level in the bottle is required from time to time. When the saline liquid in the bottle is fully consumed, and the bottle is not replaced or the infusion process stopped immediately, the difference between the patient's blood pressure and the empty saline bottle could cause an outward rush of blood into the saline.
Keywords: Fill level of bottles; Saline solution; Sodium chloride liquid; Visual monitoring.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships which have, or could be perceived to have, influenced the work reported in this article.
Figures







References
-
- Lindblad T., Kinser J.M. Springer; Berlin, Heidelberg: 2013. NumPy, SciPy and Python Image Library. In Image Processing using Pulse-Coupled Neural Networks; pp. 35–56.
-
- Chollet F. Keras Blog; 2016. Building Powerful Image Classification Models using very Little Data.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

