Role of collectin-11 in innate defence against uropathogenic Escherichia coli infection
- PMID: 33241978
- PMCID: PMC7780352
- DOI: 10.1177/1753425920974766
Role of collectin-11 in innate defence against uropathogenic Escherichia coli infection
Abstract
Classical collectins (surfactant protein A and D) play a significant role in innate immunity and host defence in uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC)-induced urinary tract infection (UTI). However, the functions of collectin-11 (CL-11) with respect to UPEC and UTI remain largely unexplored. This study aimed to investigate the effect of CL-11 on UPEC and its role in UTI. We further examined its modulatory effect on inflammatory reactions in proximal tubular epithelial cells (PTECs). The present study provides evidence for the effect of CL-11 on the growth, agglutination, binding, epithelial adhesion and invasion of UPEC. We found increased basal levels of phosphorylated p38 MAPK and human cytokine homologue (keratinocyte-derived chemokine) expression in CL-11 knockdown PTECs. Furthermore, signal regulatory protein α blockade reversed the increased basal levels of inflammation associated with CL-11 knockdown in PTECs. Additionally, CL-11 knockdown effectively inhibited UPEC-induced p38 MAPK phosphorylation and cytokine production in PTECs. These were further inhibited by CD91 blockade. We conclude that CL-11 functions as a mediator of innate immunity via direct antibacterial roles as well as dual modulatory roles in UPEC-induced inflammatory responses during UTI. Thus, the study findings suggest a possible function for CL-11 in defence against UTI.
Keywords: Collectin-11; innate immunity; urinary tract infection; uropathogenic Escherichia coli.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
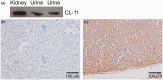

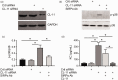
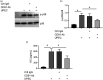
References
-
- Hamilton C, Tan L, Miethke T, et al. Immunity to uropathogens: the emerging roles of inflammasomes. Nat Rev Urol 2017; 14: 284–295. - PubMed
-
- Sihra N, Goodman A, Zakri R, et al. Nonantibiotic prevention and management of recurrent urinary tract infection. Nat Rev Urol 2018; 15: 750–776. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto J, Takahashi M, Saito A, et al. Surfactant protein A inhibits growth and adherence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli to protect the bladder from infection. J Immunol 2017; 198: 2898–2905. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

