hGC33-Modified and Sorafenib-Loaded Nanoparticles have a Synergistic Anti-Hepatoma Effect by Inhibiting Wnt Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33242103
- PMCID: PMC7691417
- DOI: 10.1186/s11671-020-03451-5
hGC33-Modified and Sorafenib-Loaded Nanoparticles have a Synergistic Anti-Hepatoma Effect by Inhibiting Wnt Signaling Pathway
Abstract
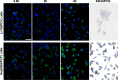
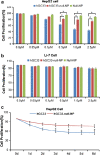
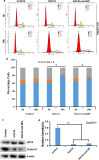
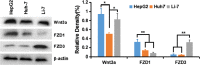
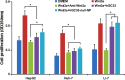
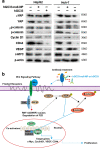
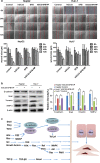
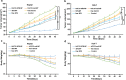
Delivery of tumor-specific inhibitors is a challenge in cancer treatment. Antibody-modified nanoparticles can deliver their loaded drugs to tumor cells that overexpress specific tumor-associated antigens. Here, we constructed sorafenib-loaded polyethylene glycol-b-PLGA polymer nanoparticles modified with antibody hGC33 to glypican-3 (GPC3 +), a membrane protein overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma. We found that hGC33-modified NPs (hGC33-SFB-NP) targeted GPC3+ hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells by specifically binding to GPC3 on the surface of HCC cells, inhibited Wnt-induced signal transduction, and inhibited HCC cells in G0/1 by down-regulating cyclin D1 expression, thus attenuating HCC cell migration by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. hGC33-SFB-NP inhibited the migration, cycle progression, and proliferation of HCC cells by inhibiting the Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway and the Wnt pathway in tandem with GPC3 molecules, respectively. hGC33-SFB-NP inhibited the growth of liver cancer in vivo and improved the survival rate of tumor-bearing mice. We conclude that hGC33 increases the targeting of SFB-NP to HCC cells. hGC33-SFB-NP synergistically inhibits the progression of HCC by blocking the Wnt pathway and the Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway.
Keywords: Glypican-3; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Targeted therapy; Wnt signal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Mingqian F, Wei G, Ruoqi W, Weizao C, Yan-Gao M, William DF, Xin WW, Dimiter SD, Mitchell H. Therapeutically targeting glypican-3 via a conformation-specific single-domain antibody in hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(12):E1083–E1091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217868110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- NO.202004j07020053/Anhui Provincial Science and Technology program
- NO. KJ2018ZD011/University Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Province
- NO. 82071862/The National Natural Science Fund of China
- 81872017/The National Natural Science Fund of China
- 81572431/The National Natural Science Fund of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

