Diagnostic accuracy of contrast-enhanced digital mammography in breast cancer detection in comparison to tomosynthesis, synthetic 2D mammography and tomosynthesis combined with ultrasound in women with dense breast
- PMID: 33242249
- PMCID: PMC7934319
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20201046
Diagnostic accuracy of contrast-enhanced digital mammography in breast cancer detection in comparison to tomosynthesis, synthetic 2D mammography and tomosynthesis combined with ultrasound in women with dense breast
Abstract
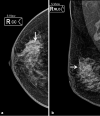
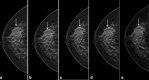
Objective: To assess the diagnostic efficacy of contrast-enhanced digital mammography (CEDM) in breast cancer detection in comparison to synthetic two-dimensional mammography (s2D MG), digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) alone and DBT supplemented with ultrasound examination in females with dense breast with histopathology as the gold-standard.
Methods: It was a prospective study, where consecutive females presenting to symptomatic breast clinic between April 2019 and June 2020 were evaluated with DBT. Females who were found to have heterogeneously dense (ACR type C) or extremely dense (ACR type D) breast composition detected on s2D MG were further evaluated with high-resolution breast ultrasound and thereafter with CEDM, but before the core biopsy or surgical excision, were included in the study. s2D MG was derived from post-processing reconstruction of DBT data set. Females with pregnancy, renal insufficiency or prior allergic reaction to iodinated contrast agent were excluded from the study. Image interpretation was done by two experienced breast radiologists and both were blinded to histological diagnosis.
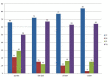
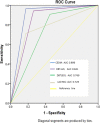
Results: This study included 166 breast lesions in130 patients with mean age of 45 ± 12 years (age range 24-72 years). There were 87 (52.4%) malignant and 79 (47.6%) benign lesions. The sensitivity of CEDM was 96.5%, significantly higher than synthetic 2D MG (75.6%, p < 0.0001), DBT alone (82.8%, p < 0.0001) and DBT + ultrasound (88.5%, p = 0.0057); specificity of CEDM was 81%, significantly higher than s2D MG (63.3%, p = 0.0002) and comparable to DBT alone (84.4%, p = 0.3586) and DBT + ultrasound (79.7%, p = 0.4135). In receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, the area under the curve was of 0.896 for CEDM, 0.841 for DBT + ultrasound, 0.769 for DBT alone and 0.729 for s2D MG.
Conclusion: CEDM is an accurate diagnostic technique for cancer detection in dense breast. CEDM allowed a significantly higher number of breast cancer detection than the s2D MG, DBT alone and DBT supplemented with ultrasonography in females with dense breast.
Advances in knowledge: CEDM is a promising novel technology with higher sensitivity and negative predictive value for breast cancer detection in females with dense breast in comparison to DBT alone or DBT supplemented with ultrasound.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Digital breast tomosynthesis and contrast-enhanced dual-energy digital mammography alone and in combination compared to 2D digital synthetized mammography and MR imaging in breast cancer detection and classification.Breast J. 2020 May;26(5):860-872. doi: 10.1111/tbj.13739. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Breast J. 2020. PMID: 31886607
-
Digital breast tomosynthesis and breast ultrasound: Additional roles in dense breasts with category 0 at conventional digital mammography.Eur J Radiol. 2016 Jan;85(1):291-296. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.09.026. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Eur J Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26499000
-
Contrast Enhanced Digital Mammography (CEDM) Helps to Safely Reduce Benign Breast Biopsies for Low to Moderately Suspicious Soft Tissue Lesions.Acad Radiol. 2020 Jul;27(7):969-976. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2019.07.020. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Acad Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31495761
-
Diagnostic performance of tomosynthesis plus synthetic mammography versus full-field digital mammography with or without tomosynthesis in breast cancer screening: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Cancer. 2025 Mar 1;156(5):969-979. doi: 10.1002/ijc.35217. Epub 2024 Oct 12. Int J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39394862 Free PMC article.
-
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) plus synthesised two-dimensional mammography (s2D) in breast cancer screening is associated with higher cancer detection and lower recalls compared to digital mammography (DM) alone: results of a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2022 Apr;32(4):2301-2312. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08308-8. Epub 2021 Oct 25. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34694451 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic performance of contrast-enhanced mammography for suspicious findings in dense breasts: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2024 Apr;13(8):e7128. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7128. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38659408 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Contrast-enhanced Mammography and Low-Energy Imaging with or without Supplemental Whole-Breast US in Breast Cancer Detection.Radiology. 2025 Mar;314(3):e242006. doi: 10.1148/radiol.242006. Radiology. 2025. PMID: 40067106
-
AI image analysis as the basis for risk-stratified screening.Jpn J Radiol. 2025 Jun;43(6):927-933. doi: 10.1007/s11604-025-01734-4. Epub 2025 Jan 11. Jpn J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39794661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of contrast-enhanced mammography in detecting malignant lesions in patients with extremely dense breasts compared to the all-densities population.Pol J Radiol. 2024 May 15;89:e240-e248. doi: 10.5114/pjr/186180. eCollection 2024. Pol J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38938658 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of Contrast-Enhanced Mammography as Breast Imaging Modality Compared to Standard Mammography and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jul 21;14(14):1575. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14141575. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sardanelli F, Podo F, D'Agnolo G, Verdecchia A, Santaquilani M, Musumeci R, et al. . Multicenter comparative multimodality surveillance of women at genetic-familial high risk for breast cancer (HIBCRIT study): interim results. Radiology 2007; 242: 698–715. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2423051965 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

