Circulating miRNA Spaceflight Signature Reveals Targets for Countermeasure Development
- PMID: 33242410
- PMCID: PMC8441986
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108448
Circulating miRNA Spaceflight Signature Reveals Targets for Countermeasure Development
Abstract
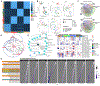
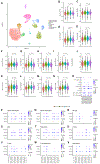
We have identified and validated a spaceflight-associated microRNA (miRNA) signature that is shared by rodents and humans in response to simulated, short-duration and long-duration spaceflight. Previous studies have identified miRNAs that regulate rodent responses to spaceflight in low-Earth orbit, and we have confirmed the expression of these proposed spaceflight-associated miRNAs in rodents reacting to simulated spaceflight conditions. Moreover, astronaut samples from the NASA Twins Study confirmed these expression signatures in miRNA sequencing, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), and single-cell assay for transposase accessible chromatin (scATAC-seq) data. Additionally, a subset of these miRNAs (miR-125, miR-16, and let-7a) was found to regulate vascular damage caused by simulated deep space radiation. To demonstrate the physiological relevance of key spaceflight-associated miRNAs, we utilized antagomirs to inhibit their expression and successfully rescue simulated deep-space-radiation-mediated damage in human 3D vascular constructs.
Keywords: NASA; Twins Study; antagomirs; miRNA-seq; microRNA; microgravity; scATAC-seq; scRNA-seq; space radiation; spaceflight.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

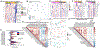
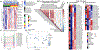

References
-
- Besnier M, Shantikumar S, Anwar M, Dixit P, Chamorro-Jorganes A, Sweaad W, Sala-Newby G, Madeddu P, Thomas AC, Howard L, et al. (2019). miR-15a/-16 Inhibit Angiogenesis by Targeting the Tie2 Coding Sequence: Therapeutic Potential of a miR-15a/16 Decoy System in Limb Ischemia. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 17, 49–62. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

