Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on testing services for HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections in the WHO European Region, March to August 2020
- PMID: 33243354
- PMCID: PMC7693166
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.47.2001943
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on testing services for HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections in the WHO European Region, March to August 2020
Abstract
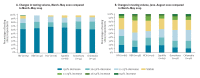
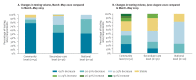
We present preliminary results of a coronavirus disease (COVID-19) impact assessment on testing for HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections in the WHO European Region. We analyse 98 responses from secondary care (n = 36), community testing sites (n = 52) and national level (n = 10). Compared to pre-COVID-19, 95% of respondents report decreased testing volumes during March-May and 58% during June-August 2020. Reasons for decreases and mitigation measures were analysed.
Keywords: COVID-19; HIV; Testing; hepatitis B infection; hepatitis C infection, sexually transmitted infections.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. Geneva: WHO. [Accessed: 10 Nov 2020]. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/?gclid=CjwKCAiA-_L9BRBQEiwA-bm5fnMSWJRDXLxVTBghc...
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Increased transmission of COVID-19 in the EU/EEA and the UK - thirteenth update. Stockholm: ECDC;23 Oct 2020. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/RRA-COVID-19-EU...
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). COVID-19 impacting HIV testing in most countries. Geneva: UNAIDS; 13 Oct 2020. Available from: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/presscentre/featurestories/2020/octo...
-
- World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe (WHO/Europe). Statement – COVID-19: taking stock and moving forward together. Copenhagen: WHO/Europe; 29 Oct 2020. Available from: https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-emergencies/coronavirus...
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections 2019. Accountability for the global health sector strategies, 2016–2021. Geneva: WHO; Jul 2019. Available from: https://www.who.int/hiv/strategy2016-2021/progress-report-2019/en/
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
