[miR-324-5p inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced proliferation of rat glomerular mesangial cells by regulating the Syk/Ras/c-fos pathway]
- PMID: 33243745
- PMCID: PMC7704383
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.11.06
[miR-324-5p inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced proliferation of rat glomerular mesangial cells by regulating the Syk/Ras/c-fos pathway]
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of miR-324-5p on the proliferation of rat glomerular mesangial (HBZY-1) cells and the role of Syk/Ras/c-fos signaling pathway in mediating this effect.
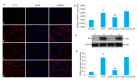
Methods: HBZY-1 cells cultured in vitro were transiently transfected with miR-324-5p mimics or miR-324-5p-mimics-NC followed by treatment with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). MTT assay was used to detect the proliferation activity of HBZY-1 cells, and RT-qPCR was used to detect the expressions of miR-324-5p and the mRNA expressions of Syk, Ras, MEK1/2, ERK1/2 and c-fos mRNA. The protein expressions of p-Syk, Ras, p-MEK1/2, p-ERK1/2 and c-Fos were detected by Western blotting and immunofluorescence assay.
Results: MTT assay showed that exposure to LPS significantly enhanced the proliferative activity of HBZY-1 cells. Compared with the cells treated with LPS and LPS + mimics NC, the cells transfected with miR-324-5p mimics prior to LPS exposure exhibited significantly lowered proliferative activity. Transfection with miR-324-5p mimics significantly lowered the mRNA expressions of Syk, Ras, MEK1/2, ERK1/2 and c-fos and the protein expressions of p-Syk, Ras, MEK1/2, ERK1/2 and c-Fos (P < 0.05), and reduced numbers of cells positive for p-Syk, Ras, p-MEK1/2, p-ERK1/2 and c-Fos proteins following LPS exposure.
Conclusions: miR-324-5p can inhibit the proliferation of rat chronic glomerulonephritis cells induced by LPS by inhibiting Syk/Ras/c-fos signaling pathway and may potentially serve as a diagnostic indicator and a therapeutic target for chronic glomerulonephritis.
目的: 探讨miR-324-5p调控Syk/Ras/c-fos信号通路对大鼠肾小球系膜(HBZY-1)细胞增殖能力的影响。
方法: 体外培养HBZY-1细胞;设计并合成miR-324-5p mimics,miR-324-5p mimics-NC片段;采用Lipo3000试剂盒瞬时转染miR-324-5p mimics,miR-324-5p mimics-NC片段至脂多糖(LPS)诱导的HBZY-1细胞内,RT-qPCR验证转染效率;将HBZY-1细胞分为对照组(生理盐水),LPS组(LPS 0.5 μg/mL),LPS+mimics组(LPS 0.5 μg/mL+miR-324-mimics),LPS+mimics-NC组(LPS 0.5 μg/mL+miR-324-mimics-NC);MTT法检测各组HBZY-1细胞增殖活性;RT-qPCR法检测各组细胞miR-324-5p及Syk、Ras、MEK1/2、ERK1/2、c-fos mRNA的表达;Western blot和免疫荧光法检测各组细胞p-Syk、Ras、p-MEK1/2、p-ERK1/2、c-fos蛋白的表达。
结果: MTT结果显示,LPS组细胞增殖水平较正常组显著升高,与LPS组及LPS+mimics-NC组相比,LPS+mimics组细胞增殖能力降低;RT-qPCR结果显示,LPS+mimics组中miR-324-5p表达明显高于LPS组及LPS+mimics-NC组,且LPS+mimics组中Syk、Ras、MEK1/2、ERK1/2、c-fos mRNA的表达显著低于LPS组及LPS+mimics-NC组, 差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05);Western Blot结果显示,与LPS组及LPS+mimics-NC组相比LPS+mimics组中p-Syk、Ras、p-MEK1/2、p-ERK1/2、c-fos蛋白表达显著降低,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05);免疫荧光结果显示,与LPS组及LPS+mimics-NC组相比,LPS+mimics组p-Syk、Ras、p-MEK1/2、p-ERK1/2、c-fos蛋白标记细胞数目明显减少。
结论: miR-324-5p可通过抑制Syk/Ras/c-fos信号通路降低LPS诱导的慢性肾小球肾炎细胞的增殖活性,miR-324-5p有望成为慢性肾小球肾炎诊断和治疗的潜在靶标。
Keywords: Chronic glomerulonephritis; Syk/Ras/c-fos signaling pathway; cell proliferation; miR-324-5p.
Figures






References
-
- 杨 倩春, 杨 霓芝. 急性肾小球肾炎病因病机探讨. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lnzyxyxb2.... 辽宁中医学院学报. 2003;1:13. [杨倩春, 杨霓芝.急性肾小球肾炎病因病机探讨[J].辽宁中医学院学报, 2003, 1: 13.]
-
- 卢 作奎, 许 为佳, 史 秀岩. 基于WNT/β-catenin信号通路研究DMBT1调控慢性肾小球肾炎发生发展的作用机制. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lcszbzz20.... 临床肾脏病杂志. 2020;20(4):297–302. [卢作奎, 许为佳, 史秀岩.基于WNT/β-catenin信号通路研究DMBT1调控慢性肾小球肾炎发生发展的作用机制[J].临床肾脏病杂志, 2020, 20(4): 297-302.]
-
- Decleves A, Sharma K. Novel targets of antifibrotic and antiinflammatory treatment in CKD. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014;10(5):257–67. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2014.31. [Decleves A, Sharma K. Novel targets of antifibrotic and antiinflammatory treatment in CKD[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2014, 10(5): 257-67.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
-
杨莉.福辛普利对肾小球系膜细胞增殖的影响[D].中国医科大学, 2007.
-
-
- Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P, et al. miRWalk-Database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by walking the genes of three genomes. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2304897. J Biomed Informatics. 2011;44(5):839–47. [Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P, et al. miRWalk-Database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by walking the genes of three genomes [J]. J Biomed Informatics, 2011, 44(5): 839-47.] - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
