Modeling the transmission dynamics of COVID-19 epidemic: a systematic review
- PMID: 33243940
- PMCID: PMC7718076
- DOI: 10.7555/JBR.34.20200119
Modeling the transmission dynamics of COVID-19 epidemic: a systematic review
Abstract
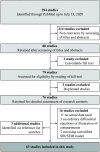
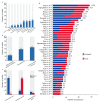
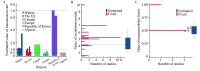
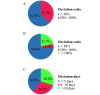
The outbreak and rapid spread of COVID-19 has become a public health emergency of international concern. A number of studies have used modeling techniques and developed dynamic models to estimate the epidemiological parameters, explore and project the trends of the COVID-19, and assess the effects of intervention or control measures. We identified 63 studies and summarized the three aspects of these studies: epidemiological parameters estimation, trend prediction, and control measure evaluation. Despite the discrepancy between the predictions and the actuals, the dynamic model has made great contributions in the above three aspects. The most important role of dynamic models is exploring possibilities rather than making strong predictions about longer-term disease dynamics.
Keywords: COVID-19; SEIR model; SIR model; coronavirus; epidemiology modeling; transmission dynamic model.
Figures
References
-
-
Statement on the second meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee regarding the outbreak of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV)[EB/OL]. [2020-01-30]. https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-meeting-of-the-international-health-regulations-(2....
-
-
-
Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports[EB/OL]. [2020-01-21]. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports.
-
-
-
Ma S, Xia YC. Mathematical understanding of infectious disease dynamics[M]. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Company, 2008.
-
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources