UMI-linked consensus sequencing enables phylogenetic analysis of directed evolution
- PMID: 33243970
- PMCID: PMC7691348
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19687-9
UMI-linked consensus sequencing enables phylogenetic analysis of directed evolution
Abstract
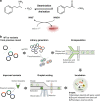
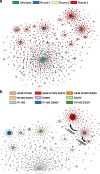
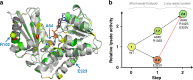
The success of protein evolution campaigns is strongly dependent on the sequence context in which mutations are introduced, stemming from pervasive non-additive interactions between a protein's amino acids ('intra-gene epistasis'). Our limited understanding of such epistasis hinders the correct prediction of the functional contributions and adaptive potential of mutations. Here we present a straightforward unique molecular identifier (UMI)-linked consensus sequencing workflow (UMIC-seq) that simplifies mapping of evolutionary trajectories based on full-length sequences. Attaching UMIs to gene variants allows accurate consensus generation for closely related genes with nanopore sequencing. We exemplify the utility of this approach by reconstructing the artificial phylogeny emerging in three rounds of directed evolution of an amine dehydrogenase biocatalyst via ultrahigh throughput droplet screening. Uniquely, we are able to identify lineages and their founding variant, as well as non-additive interactions between mutations within a full gene showing sign epistasis. Access to deep and accurate long reads will facilitate prediction of key beneficial mutations and adaptive potential based on in silico analysis of large sequence datasets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gencore: an efficient tool to generate consensus reads for error suppressing and duplicate removing of NGS data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Dec 27;20(Suppl 23):606. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-3280-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31881822 Free PMC article.
-
Speeding up enzyme discovery and engineering with ultrahigh-throughput methods.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018 Feb;48:149-156. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2017.12.010. Epub 2018 Feb 3. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 29413955 Review.
-
On synergy between ultrahigh throughput screening and machine learning in biocatalyst engineering.Faraday Discuss. 2024 Sep 11;252(0):89-114. doi: 10.1039/d4fd00065j. Faraday Discuss. 2024. PMID: 39133073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting models of molecular evolution to efficiently direct protein engineering.J Mol Evol. 2011 Feb;72(2):193-203. doi: 10.1007/s00239-010-9415-2. Epub 2010 Dec 4. J Mol Evol. 2011. PMID: 21132281 Free PMC article.
-
How mutational epistasis impairs predictability in protein evolution and design.Protein Sci. 2016 Jul;25(7):1260-72. doi: 10.1002/pro.2876. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Protein Sci. 2016. PMID: 26757214 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ultra-High-Throughput Absorbance-Activated Droplet Sorting for Enzyme Screening at Kilohertz Frequencies.Anal Chem. 2023 Mar 14;95(10):4597-4604. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c04144. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 36848587 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous evolution of user-defined genes at 1 million times the genomic mutation rate.Science. 2024 Nov 8;386(6722):eadm9073. doi: 10.1126/science.adm9073. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Science. 2024. PMID: 39509492
-
A Titratable Cell Lysis-on-Demand System for Droplet-Compartmentalized Ultrahigh-Throughput Screening in Functional Metagenomics and Directed Evolution.ACS Synth Biol. 2021 Aug 20;10(8):1882-1894. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.1c00084. Epub 2021 Jul 14. ACS Synth Biol. 2021. PMID: 34260196 Free PMC article.
-
High-Throughput Steady-State Enzyme Kinetics Measured in a Parallel Droplet Generation and Absorbance Detection Platform.Anal Chem. 2022 Dec 6;94(48):16701-16710. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c03164. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Anal Chem. 2022. PMID: 36417687 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous directed evolution of a compact CjCas9 variant with broad PAM compatibility.Nat Chem Biol. 2024 Mar;20(3):333-343. doi: 10.1038/s41589-023-01427-x. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Nat Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 37735239 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

