Salt-responsive transcriptome analysis of triticale reveals candidate genes involved in the key metabolic pathway in response to salt stress
- PMID: 33244037
- PMCID: PMC7691987
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-77686-8
Salt-responsive transcriptome analysis of triticale reveals candidate genes involved in the key metabolic pathway in response to salt stress
Abstract
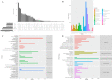
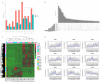
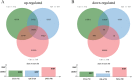
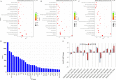
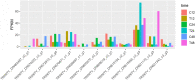
Triticale is tolerant of many environmental stresses, especially highly resistant to salt stress. However, the molecular regulatory mechanism of triticale seedlings under salt stress conditions is still unclear so far. In this study, a salt-responsive transcriptome analysis was conducted to identify candidate genes or transcription factors related to salt tolerance in triticale. The root of salt-tolerant triticale cultivars TW004 with salt-treated and non-salt stress at different time points were sampled and subjected to de novo transcriptome sequencing. Total 877,858 uniquely assembled transcripts were identified and most contigs were annotated in public databases including nr, GO, KEGG, eggNOG, Swiss-Prot and Pfam. 59,280, 49,345, and 85,922 differentially expressed uniquely assembled transcripts between salt treated and control triticale root samples at three different time points (C12_vs_T12, C24_vs_T24, and C48_vs_T48) were identified, respectively. Expression profile and functional enrichment analysis of DEGs found that some DEGs were significantly enriched in metabolic pathways related to salt tolerance, such as reduction-oxidation pathways, starch and sucrose metabolism. In addition, several transcription factor families that may be associated with salt tolerance were also identified, including AP2/ERF, NAC, bHLH, WRKY and MYB. Furthermore, 14 DEGs were selected to validate the transcriptome profiles via quantitative RT-PCR. In conclusion, these results provide a foundation for further researches on the regulatory mechanism of triticale seedlings adaptation to salt stress in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Rhoades J, Loveday J. Salinity in irrigated agriculture. Agronomy. 1990;30:1089–1142.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

