White matter microarchitecture and structural network integrity correlate with children intelligence quotient
- PMID: 33244043
- PMCID: PMC7691327
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-76528-x
White matter microarchitecture and structural network integrity correlate with children intelligence quotient
Abstract
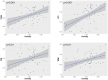
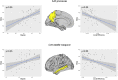
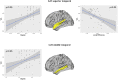
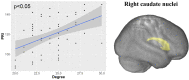
The neural substrate of high intelligence performances remains not well understood. Based on diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) which provides microstructural information of white matter fibers, we proposed in this work to investigate the relationship between structural brain connectivity and intelligence quotient (IQ) scores. Fifty-seven children (8-12 y.o.) underwent a MRI examination, including conventional T1-weighted and DTI sequences, and neuropsychological testing using the fourth edition of Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC-IV), providing an estimation of the Full-Scale Intelligence Quotient (FSIQ) based on four subscales: verbal comprehension index (VCI), perceptual reasoning index (PRI), working memory index (WMI), and processing speed index (PSI). Correlations between the IQ scores and both graphs and diffusivity metrics were explored. First, we found significant correlations between the increased integrity of WM fiber-bundles and high intelligence scores. Second, the graph theory analysis showed that integration and segregation graph metrics were positively and negatively correlated with WISC-IV scores, respectively. These results were mainly driven by significant correlations between FSIQ, VCI, and PRI and graph metrics in the temporal and parietal lobes. In conclusion, these findings demonstrated that intelligence performances are related to the integrity of WM fiber-bundles as well as the density and homogeneity of WM brain networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Basten U, Hilger K, Fiebach CJ. Where smart brains are different: a quantitative meta-analysis of functional and structural brain imaging studies on intelligence. Intelligence. 2015 doi: 10.1016/j.intell.2015.04.009. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

