Galectin-1 is associated with the severity of coronary artery disease and adverse cardiovascular events in patients undergoing coronary angiography
- PMID: 33244142
- PMCID: PMC7692553
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-77804-6
Galectin-1 is associated with the severity of coronary artery disease and adverse cardiovascular events in patients undergoing coronary angiography
Abstract
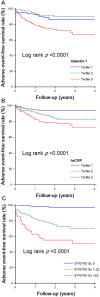
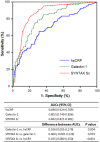
Galectin-1, a β-galactoside-binding lectin mediating inflammation and neovascularization, is reported to attenuate ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. But its role in stable coronary artery disease (CAD) has not been fully elucidated. This study aimed to identify the relationship between the circulating galectin-1 level and the severity of CAD in patients with suspected CAD. Pre-procedure galectin-1 and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) concentrations were measured in 834 subjects who underwent scheduled coronary angiography. Subjects were grouped into tertiles of the galectin-1 levels. SYNTAX scores were calculated to evaluate the severity of CAD. All patients were followed until January 2019 or the occurrence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). Patients with higher galectin-1 concentrations were older; had greater prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and heart failure; and were more likely to present with higher hs-CRP levels and SYNTAX scores. During the follow-up period of 1.3 ± 1.1 years, patients in the highest tertile of galectin-1 were associated with a greater risk of MACE after adjustment for age, sex, comorbidities, co-medications, serum levels of hemoglobin, creatinine, hs-CRP, ejection fraction, SYNTAX scores, and revascularization modalities (adjusted hazard ratio 10.95, 95% confidence interval 2.29-52.47, p = 0.003). Galectin-1 showed better discriminatory performance than hs-CRP, and non-inferior performance to SYNTAX scores, in predicting the incidence of MACE.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Barondes SH, Cooper DN, Gitt MA, Leffler H. Galectins, structure and function of a large family of animal lectins. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:20807–20810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

