Focus on gastroesophageal reflux disease in patients with cystic fibrosis
- PMID: 33244195
- PMCID: PMC7656210
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i41.6322
Focus on gastroesophageal reflux disease in patients with cystic fibrosis
Abstract
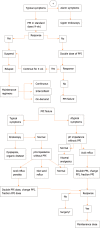
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common gastrointestinal disorder in cystic fibrosis (CF), and based on various studies, its prevalence is elevated since childhood. There are several pathogenetic mechanisms on the basis of association between CF and GERD. However, there are no specific guidelines for GERD in CF patients, so diagnosis is based on guidelines performed on patients not affected by CF. The aim of this review is to provide the pathophysiology, diagnostic and therapeutic options, complications, and future directions in the management of GERD patients with CF.
Keywords: Adult; Children; Cystic Fibrosis; Gastroesophageal reflux.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
References
-
- Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, Dent J, Jones R Global Consensus Group. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1900–20; quiz 1943. - PubMed
-
- Gustafsson PM, Fransson SG, Kjellman NI, Tibbling L. Gastro-oesophageal reflux and severity of pulmonary disease in cystic fibrosis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1991;26:449–456. - PubMed
-
- Feigelson J, Sauvegrain J. [Letter: Gastro-esophageal reflux in mucoviscidosis] Nouv Presse Med. 1975;4:2729–2730. - PubMed
-
- Pauwels A, Blondeau K, Mertens V, Farre R, Verbeke K, Dupont LJ, Sifrim D. Gastric emptying and different types of reflux in adult patients with cystic fibrosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;34:799–807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical