Preclinical and Clinical Development of Therapeutic Antibodies Targeting Functions of CD47 in the Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 33244513
- PMCID: PMC7687918
- DOI: 10.1093/abt/tbaa017
Preclinical and Clinical Development of Therapeutic Antibodies Targeting Functions of CD47 in the Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
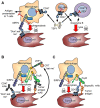
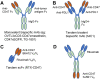
CD47 is a ubiquitously expressed cell surface glycoprotein that functions as a signaling receptor for thrombospondin-1 and as the counter-receptor for signal regulatory protein-α (SIRPα). Engaging SIRPα on macrophages inhibits phagocytosis, and CD47 thereby serves as a physiological marker of self. However, elevated CD47 expression on some cancer cells also protects tumors from innate immune surveillance and limits adaptive antitumor immunity via inhibitory SIRPα signaling in antigen presenting cells. CD47 also mediates inhibitory thrombospondin-1 signaling in vascular cells, T cells, and NK cells, and blocking inhibitory CD47 signaling on cytotoxic T cells directly increases tumor cell killing. Therefore, CD47 functions as an innate and adaptive immune checkpoint. These findings have led to the development of antibodies and other therapeutic approaches to block CD47 functions in the tumor microenvironment. Preclinical studies in mice demonstrated that blocking CD47 can limit the growth of hematologic malignancies and solid tumors and enhance the efficacy of conventional chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and some targeted cancer therapies. Humanized CD47 antibodies are showing promise in early clinical trials, but side effects related to enhanced phagocytic clearance of circulating blood cells remain a concern. Approaches to circumvent these include antibody preloading strategies, development of antibodies that recognize tumor-specific epitopes of CD47, SIRPα antibodies, and bivalent antibodies that restrict CD47 blockade to specific tumor cells. Preclinical and clinical development of antibodies and related biologics that inhibit CD47/SIRPα signaling are reviewed, including strategies to combine these agents with various conventional and targeted therapeutics to improve patient outcome for various cancers.
Keywords: bifunctional antibodies; humanized CD47 antibodies; immune checkpoint; immunotherapy; signal regulatory protein-α.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeting the myeloid checkpoint receptor SIRPα potentiates innate and adaptive immune responses to promote anti-tumor activity.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Nov 30;13(1):160. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00989-w. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33256806 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer immunotherapy targeting the CD47/SIRPα axis.Eur J Cancer. 2017 May;76:100-109. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.02.013. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Eur J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28286286 Review.
-
BYON4228 is a pan-allelic antagonistic SIRPα antibody that potentiates destruction of antibody-opsonized tumor cells and lacks binding to SIRPγ on T cells.J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Apr;11(4):e006567. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-006567. J Immunother Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37068796 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical characterization of the novel anti-SIRPα antibody BR105 that targets the myeloid immune checkpoint.J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Mar;10(3):e004054. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-004054. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35256517 Free PMC article.
-
The CD47-SIRPα signaling axis as an innate immune checkpoint in cancer.Immunol Rev. 2017 Mar;276(1):145-164. doi: 10.1111/imr.12527. Immunol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28258703 Review.
Cited by
-
CD47 as a promising therapeutic target in oncology.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 22;13:757480. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.757480. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36081498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fatty Acids, CD36, Thrombospondin-1, and CD47 in Glioblastoma: Together and/or Separately?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 6;23(2):604. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020604. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune pathway through endometriosis to ovarian cancer.World J Clin Oncol. 2024 Apr 24;15(4):496-522. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i4.496. World J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38689629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Affinity Engineered Anti-CD47 Antibody With Improved Therapeutic Index That Preserves Erythrocytes and Normal Immune Cells.Front Oncol. 2022 May 19;12:884196. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.884196. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35664753 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities and challenges of CD47-targeted therapy in cancer immunotherapy.Oncol Res. 2023 Nov 15;32(1):49-60. doi: 10.32604/or.2023.042383. eCollection 2023. Oncol Res. 2023. PMID: 38188674 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Matlung, HL, Szilagyi, K, Barclay, NA, et al. . The CD47-SIRPalpha signaling axis as an innate immune checkpoint in cancer. Immunol Rev 2017; 276: 145–64. - PubMed
-
- Okazawa, H, Motegi, S, Ohyama, N, et al. . Negative regulation of phagocytosis in macrophages by the CD47-SHPS-1 system. J Immunol 2005; 174: 2004–11. - PubMed
-
- Oldenborg, PA, Zheleznyak, A, Fang, YF, et al. . Role of CD47 as a marker of self on red blood cells. Science 2000; 288: 2051–4. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
