Circ_0008039 supports breast cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and glycolysis by regulating the miR-140-3p/SKA2 axis
- PMID: 33244865
- PMCID: PMC7858101
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12862
Circ_0008039 supports breast cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and glycolysis by regulating the miR-140-3p/SKA2 axis
Abstract
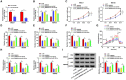
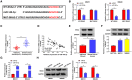
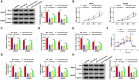
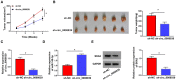
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been shown to modulate gene expression and participate in the development of multiple malignancies. The purpose of this study was to investigate the role of circ_0008039 in breast cancer (BC). The expression of circ_0008039, miR-140-3p, and spindle and kinetochore-associated protein 2 (SKA2) was detected by qRT-PCR. Cell viability, colony formation, migration, and invasion were evaluated using methylthiazolyldiphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, colony formation assay, and transwell assay, respectively. Glucose consumption and lactate production were measured using commercial kits. Protein levels of hexokinase II (HK2) and SKA2 were determined by western blot. The interaction between miR-140-3p and circ_0008039 or SKA2 was verified by dual-luciferase reporter assay. Finally, a mouse xenograft model was established to investigate the roles of circ_0008039 in BC in vivo. We found that circ_0008039 and SKA2 were upregulated in BC tissues and cells, while miR-140-3p was downregulated. Knockdown of circ_0008039 suppressed BC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and glycolysis. Moreover, miR-140-3p could bind to circ_0008039 and its inhibition reversed the inhibitory effect of circ_0008039 interference on proliferation, migration, invasion, and glycolysis in BC cells. SKA2 was verified as a direct target of miR-140-3p and its overexpression partially inhibited the suppressive effect of miR-140-3p restoration in BC cells. Additionally, circ_0008039 positively regulated SKA2 expression by sponging miR-140-3p. Consistently, silencing circ_0008039 restrained tumor growth via increasing miR-140-3p and decreasing SKA2. In conclusion, circ_0008039 downregulation suppressed BC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and glycolysis partially through regulating the miR-140-3p/SKA2 axis, providing an important theoretical basis for treatment of BC.
Keywords: SKA2; breast cancer; circ_0008039; miR-140-3p.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA & Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68, 394–424. - PubMed
-
- Ewertz M & Jensen AB (2011) Late effects of breast cancer treatment and potentials for rehabilitation. Acta Oncol 50, 187–193. - PubMed
-
- Ojha R, Nandani R, Chatterjee N & Prajapati VK (2018) Emerging role of circular RNAs as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of human diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol 1087, 141–157. - PubMed
-
- Zhang HD, Jiang LH, Sun DW, Hou JC & Ji ZL (2018) CircRNA: a novel type of biomarker for cancer. Breast Cancer 25, 1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

