Software-assisted US/MRI fusion-targeted biopsy for prostate cancer
- PMID: 33245067
- PMCID: PMC8023072
- DOI: 10.23750/abm.v91i10-S.10273
Software-assisted US/MRI fusion-targeted biopsy for prostate cancer
Abstract
Background: Prostate cancer is the first cancer diagnosis in men. European Association of Urology (EAU) Guidelines for Prostate Cancer underline the importance of screening, performed through PSA testing on all men with more than 50 years of age and before on men with risk factors. The diagnosis is still histopathologic, and it is done on the basis of the findings on biopsy samples.
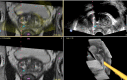
Materials and methods: Fusion biopsy is a relatively new technique that allows the operator to perform the biopsies in office instead of the MRI gantry, without losing the detection capability of MRI. The T2-wighted images obtained during a previous mpMRI are merged with the real-time ones of the TRUS.
Results: Fusion biopsy in comparison with the systematic standard biopsy has a better detection rate of clinically significant cancers and of any cancers.
Conclusion: EAU 2020 guidelines still do offer a list of indications of when the biopsy should be performed, but it still appeared to be overperformed. The aim of our study is to underline how, in accordance with the recent literature result, fusion biopsy has showed a better detection rate of any cancer and clinically significant disease with a reduced numbers of samplings, and no substantial difference between the multiple software.
Conflict of interest statement
Each author declares that he or she has no commercial associations (e.g. consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangement etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R. L, Miller K. D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2019;69:7–34. - PubMed
-
- EAU. EAU 2020 Guidelines for Prostate. Cancer. 2020. https://uroweb.org/guideline/prostate-cancer/
-
- Djavan B, Margreiter M. Biopsy standards for detection of prostate cancer. World J. Urol. 2007;25:11–17. - PubMed
-
- Roobol M. J, et al. A Risk-Based Strategy Improves Prostate-Specific Antigen-Driven Detection of Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2010;57:79–85. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

