Hypnotherapy for Irritable Bowel Syndrome-Type Symptoms in Patients with Quiescent Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Randomized, Controlled Trial
- PMID: 33245332
- PMCID: PMC8256629
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaa241
Hypnotherapy for Irritable Bowel Syndrome-Type Symptoms in Patients with Quiescent Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Randomized, Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background and aims: Many inflammatory bowel disease [IBD] patients in remission have persisting symptoms, compatible with irritable bowel syndrome [IBS-type symptoms]. We aimed to compare the effectiveness of gut-directed hypnotherapy vs standard medical treatment [SMT] for IBS-type symptoms in IBD patients.
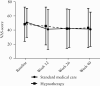
Methods: In this multicentre, randomized, controlled, open-label trial, patients aged 12-65 years with IBD in clinical remission [global assessment] and biochemical remission [faecal calprotectin ≤100 µg/g, or ≤200 µg/g without inflammation at endoscopy] with IBS according to Rome III criteria were randomized to hypnotherapy or SMT. Primary outcome was the proportion with ≥50% reduction on a visual analog scale for symptom severity, as measured with the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Severity Scoring System [IBS-SSS] at week 40 [i.e. 6 months after finishing the intervention], compared to baseline. Secondary outcomes included total IBS-SSS score, quality of life, adequate relief, IBS-related cognitions, and depression and anxiety scores.
Results: Eighty patients were included, of whom 70 received at least one session of the allocated treatment and were included in the modified intention-to-treat-population. Seven patients were excluded because of missing baseline data required for the primary outcome. The primary outcome was met in nine [27%] of 33 patients randomized to SMT and nine [30%] of 30 patients randomized to hypnotherapy [p = 0.81]. Adequate relief was reported in 60% and 40% of subjects, respectively. Exploratory analyses of secondary outcomes revealed no apparent differences between the two treatment groups.
Conclusions: Hypnotherapy was not superior to SMT in the treatment of IBS-type symptoms in IBD patients. Both treatment strategies are reasonable options from a clinical perspective.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; IBS-like symptoms; IBS-type symptoms; gut-directed hypnotherapy; hypnotherapy; inflammatory bowel disease; irritable bowel syndrome; ulcerative colitis.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation.
Figures
Comment in
-
Body, Soul, and Hypnotherapy.J Crohns Colitis. 2021 Jul 5;15(7):1083-1084. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaa266. J Crohns Colitis. 2021. PMID: 33619514 No abstract available.
References
-
- Halpin SJ, Ford AC. Prevalence of symptoms meeting criteria for irritable bowel syndrome in inflammatory bowel disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 2012;107:1474–82. - PubMed
-
- Berrill JW, Sadlier M, Hood K, Green JT. Mindfulness-based therapy for inflammatory bowel disease patients with functional abdominal symptoms or high perceived stress levels. J Crohns Colitis 2014;8:945–55. - PubMed
-
- Piche T, Pishvaie D, Tirouvaziam D, et al. . Osteopathy decreases the severity of IBS-like symptoms associated with Crohn’s disease in patients in remission. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014;26:1392–8. - PubMed
-
- Hallert C, Kaldma M, Petersson BG. Ispaghula husk may relieve gastrointestinal symptoms in ulcerative colitis in remission. Scand J Gastroenterol 1991;26:747–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous