Complicated pyelonephritis associated with chronic renal stone disease
- PMID: 33245481
- PMCID: PMC8007507
- DOI: 10.1007/s11547-020-01315-7
Complicated pyelonephritis associated with chronic renal stone disease
Abstract
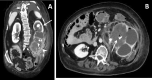
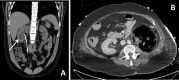
Purpose: This article reviews imaging manifestations of complicated pyelonephritis associated with chronic renal stones disease, in particular xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (XGP) and emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN), as potential mimics of other renal diseases and malignances and provides helpful tips and differentiating features that may alert the radiologist to suspect a diagnosis of infection.
Materials and methods: A retrospective review of the records from 6 adult patients (5 females and 1 male, mean age 72,3 years) with diagnosis of XGP associated with chronic nephrolithiasis and 7 adult patients (6 females and 1 male, mean age 59,3 years) with diagnosis of EPN associated with chronic nephrolithiasis from January 2010 to January 2020 was carried out. Computed tomography urography (CTU) with at least an unenhanced scan, and the parenchymal and excretory phases after contrast medium administration performed at our Teaching Hospital were included. When available images related to conventional radiography, ultrasound (US) and magnetic resonance imaging of the same patients, the comparison with CTU images was carried out.
Conclusion: A possible diagnosis of XGP or EPN must always be taken into account when a pyelonephritis is associated with untreated kidney stones, especially whenever clinical presentation is atypical, current therapy is not effective and imaging shows features of dubious interpretation. Due to their rarity and atypical presentation, a multidisciplinary approach is required and an expert radiologist represents a key figure in the multidisciplinary team as he can help to differentiate between benign and malignant lesions and thus avoid unnecessary radical surgical procedures.
Keywords: Complicated pyelonephritis; Emphysematous pyelonephritis; Nephrolithiasis; Renal stone disease; Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Figures




References
-
- Lin SY, Lin CL, Chang CH, Wu HC, Chen WC, Wang IK, Liu YL, Sung FC, Chang YJ, Kao CH. Comparative risk of chronic kidney diseases in patients with urolithiasis and urological interventions: a longitudinal population-based study. Urolithiasis. 2017;45(5):465–472. doi: 10.1007/s00240-016-0929-y. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

