Type I interferon in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 33246136
- PMCID: PMC8054829
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2020.10.014
Type I interferon in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
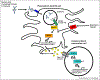
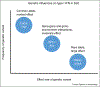
Type I interferon (IFN) is a primary pathogenic factor in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Gain-of-function genetic variants in the type I IFN pathway have been associated with risk of disease. Common polygenic as well as rare monogenic influences on type I IFN have been demonstrated, supporting a complex genetic basis for high IFN in many SLE patients. Both SLE-associated autoantibodies and high type I IFN can be observed in the pre-disease state. Patients with SLE and evidence of high type I IFN have more active disease and a greater propensity to nephritis and other severe manifestations. Despite the well-established association between type I IFN and SLE, the specific triggers of type I IFN production, the mechanisms by which IFNs help perpetuate the cycle of autoreactive cells and autoantibody production are not completely clear. This review provides an updated overview of type I IFN in SLE pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and current therapeutic strategies targeting this pathway.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Tsokos GC, Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med, 2011. 365(22): p. 2110–21. - PubMed
-
-
Weckerle CE and Niewold TB, The unexplained female predominance of systemic lupus erythematosus: clues from genetic and cytokine studies. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol, 2011. 40(1): p. 42–9.
* Largest study to date of functional type I IFN levels in lupus patients, demonstrating differences between ancestral backgrounds and strong association with serological profiles.
-
-
-
Baechler EC, et al. , Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2003. 100(5): p. 2610–5.
* Early study documenting the IFN signature in SLE, also makes the point that type I and type II IFNs are difficult to separate by their downstream signatures.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

