COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of current literature
- PMID: 33246166
- PMCID: PMC7666542
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trre.2020.100588
COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of current literature
Abstract
Severe acute respiratory virus syndrome 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has led to a worldwide pandemic. Early studies in solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients suggested a wide variety of presentations, however, there remains a paucity of robust data in this population. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of SOT recipients with SARS-CoV-2 infection from January 1st t October 9th, 2020. Pooled incidence of symptoms, treatments and outcomes were assessed. Two hundred and fifteen studies were included for systematic review and 60 for meta-analysis. We identified 2,772 unique SOT recipients including 1,500 kidney, 505 liver, 141 heart and 97 lung. Most common presenting symptoms were fever and cough in 70.2% and 63.8% respectively. Majority (81%) required hospital admission. Immunosuppressive medications, especially antimetabolites, were decreased in 76.2%. Hydroxychloroquine and interleukin six antagonists were administered in59.5% and 14.9% respectively, while only few patients received remdesivir and convalescent plasma. Intensive care unit admission was 29% from amongst hospitalized patients. Only few studies reported secondary infections. Overall mortality was 18.6%. Our analysis shows a high incidence of hospital admission in SOT recipients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. As management of SARS-CoV-2 continues to evolve, long-term outcomes among SOT recipients should be assessed in future studies.
Keywords: COVID-19; Immunosuppression; Meta-analysis; SARS-CoV-2; Solid organ transplant; Systematic review.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors of this manuscript declare no competing conflicts of interest.
Figures
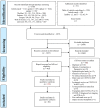
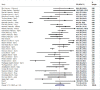

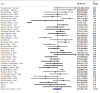
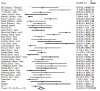




Comment in
-
Coinfection of COVID-19 and pneumocystosis in a patient after kidney transplantation.Pol Arch Intern Med. 2021 Jun 29;131(6):566-567. doi: 10.20452/pamw.15996. Epub 2021 May 11. Pol Arch Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33973748 No abstract available.
References
-
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) World Health Organization; 2020. Situation Report.
-
- Kumar D., Ferreira V.H., Blumberg E., Silveira F., Cordero E., Perez-Romero P. A 5-Year Prospective Multicenter Evaluation of Influenza Infection in Transplant Recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;67:1322–1329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

