Exosomes from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate histone-induced acute lung injury by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway in endothelial cells
- PMID: 33246503
- PMCID: PMC7691956
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-020-02015-9
Exosomes from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate histone-induced acute lung injury by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway in endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), including adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs), have been shown to attenuate organ damage in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and sepsis; however, the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. In this study, we aimed to explore the potential roles and molecular mechanisms of action of ADSCs in histone-induced endothelial damage.
Methods: Male C57BL/6 N mice were intravenously injected with ADSCs, followed by histones or a vehicle. The mice in each group were assessed for survival, pulmonary vascular permeability, and histological changes. A co-culture model with primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) exposed to histones was used to clarify the paracrine effect of ADSCs. Overexpression and inhibition of miR-126 ADSCs were also examined as causative factors for endothelial protection.
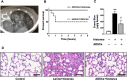
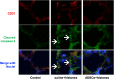
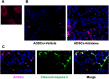
Results: The administration of ADSCs markedly improved survival, inhibited histone-mediated lung hemorrhage and edema, and attenuated vascular hyper-permeability in mice. ADSCs were engrafted in the injured lung and attenuated histone-induced endothelial cell apoptosis. ADSCs showed endothelial protection (via a paracrine effect) and Akt phosphorylation in the histone-exposed HUVECs. Notably, increased Akt phosphorylation by ADSCs was mostly mediated by exosomes in histone-induced cytotoxicity and lung damage. Moreover, the expression of miR-126 was increased in exosomes from histone-exposed ADSCs. Remarkably, the inhibition of miR-126 in ADSCs failed to increase Akt phosphorylation in histone-exposed HUVECs.
Conclusion: ADSC-derived exosomes may exert protective effects on endothelial cells via activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Acute respiratory distress syndrome; Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells; Endothelial damage; Exosomes; Histones; PI3K/Akt signaling pathway; Sepsis; miR-126.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Chang CL, Leu S, Sung HC, Zhen YY, Cho CL, Chen A, et al. Impact of apoptotic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on attenuating organ damage and reducing mortality in rat sepsis syndrome induced by cecal puncture and ligation. J Transl Med. 2012;10:244. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-244. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

