Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib for first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended 4-year follow-up of the phase III CheckMate 214 trial
- PMID: 33246931
- PMCID: PMC7703447
- DOI: 10.1136/esmoopen-2020-001079
Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib for first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended 4-year follow-up of the phase III CheckMate 214 trial
Abstract
Purpose: To report updated analyses of the phase III CheckMate 214 trial with extended minimum follow-up assessing long-term outcomes with first-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab (NIVO+IPI) versus (vs) sunitinib (SUN) in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC).
Methods: Patients with aRCC with a clear cell component were stratified by International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium risk and randomised to NIVO (3 mg/kg) plus IPI (1 mg/kg) every three weeks ×4 doses, followed by NIVO (3 mg/kg) every two weeks; or SUN (50 mg) once per day ×4 weeks (6-week cycle). Efficacy endpoints included overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS) and objective response rate (ORR) per independent radiology review committee in patients with intermediate/poor-risk disease (I/P; primary), intent-to-treat patients (ITT; secondary) and in patients with favourable-risk disease (FAV; exploratory).
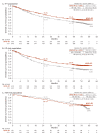
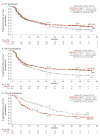
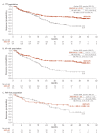
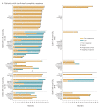
Results: Overall, 1096 patients were randomised (ITT: NIVO+IPI, n=550, SUN, n=546; I/P: NIVO+IPI, n=425, SUN, n=422; FAV: NIVO+IPI, n=125, SUN, n=124). After 4 years minimum follow-up, OS (HR; 95% CI) remained superior with NIVO+IPI vs SUN in ITT (0.69; 0.59 to 0.81) and I/P patients (0.65; 0.54 to 0.78). Four-year PFS probabilities were 31.0% vs 17.3% (ITT) and 32.7% vs 12.3% (I/P), with NIVO+IPI vs SUN. ORR remained higher with NIVO+IPI vs SUN in ITT (39.1% vs 32.4%) and I/P (41.9% vs 26.8%) patients. In FAV patients, the HRs (95% CI) for OS and PFS were 0.93 (0.62 to 1.40) and 1.84 (1.29 to 2.62); ORR was lower with NIVO+IPI vs SUN. However, more patients in all risk groups achieved complete responses with NIVO+IPI: ITT (10.7% vs 2.6%), I/P (10.4% vs 1.4%) and FAV (12.0% vs 6.5%). Probability (95% CI) of response ≥4 years was higher with NIVO+IPI vs SUN (ITT, 59% (0.51 to 0.66) vs 30% (0.21 to 0.39); I/P, 59% (0.50 to 0.67) vs 24% (0.14 to 0.36); and FAV, 60% (0.41 to 0.75) vs 38% (0.22 to 0.54)) regardless of risk category. Safety remained favourable with NIVO+IPI vs SUN.
Conclusion: After long-term follow-up, NIVO+IPI continues to demonstrate durable efficacy benefits vs SUN, with manageable safety.
Trial registration details: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02231749.
Keywords: advanced renal cell carcinoma; checkmate 214; dual checkpoint inhibition; long-term follow-up; nivolumab plus ipilimumab.
© Author (s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. Published by BMJ on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: LA reports consulting fees from Pfizer, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Ipsen, Roche, MSD, AstraZeneca, Merck, Amgen, Astellas and Exelixis; and other fees from Corvus Pharmaceuticals and Peloton Therapeutics. NMT reports research funding from BMS, Calithera Biosciences, Nektar Therapeutics, Exelixis, Pfizer, Novartis, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Mirati Therapeutics, Takeda, Epizyme and Eisai Medical Research; consulting and advisory fees from BMS, Calithera Biosciences, Nektar Therapeutics, Exelixis, Pfizer, Novartis, Eisai Medical Research, Ipsen, Lilly Oncology, Neoleukin Therapeutics, Surface Oncology, ONO Pharmaceutical and Oncorena; and travel accommodations and expenses from BMS, Calithera Biosciences, Nektar Therapeutics, Exelixis, Pfizer, Novartis, Eisai Medical Research, Ipsen, Lilly Oncology, Neoleukin Therapeutics, Surface Oncology, ONO Pharmaceutical and Oncorena. MB reports advisory and speaker fees from Roche, MSD, BMS, AstraZeneca and Sanofi. DM reports research funding from BMS, Merck, Genentech/Roche, Novartis, Peloton Therapeutics, Alkermes and Prometheus Laboratories; consulting or advisory fees from BMS, Merck, Genentech/Roche, Pfizer, Exelixis, Novartis, X4 Pharma, Array BioPharma, Peloton Therapeutics, EMD Serono, Jounce Therapeutics, Alkermes and Lilly; and other fees from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. ERP reports research funding (institutional) from BMS, AstraZeneca, Merck, Peloton Therapeutics, Pfizer and Astellas; consulting fees from AstraZeneca, BMS, Genentech, Merck, Pfizer, Clovis, Exelixis, Incyte, Seattle Genetics, Janssen, Flatiron Health, Infinity Pharma and McKesson; fees for development of educational presentations from BMS and Merck; and US Patent Application No. 14/588,503. PB reports consulting or advisory fees from BMS, Pfizer, MSD Oncology, Novartis, Ipsen, Roche and Janssen Cilag; travel accommodations and expenses from Amgen; and honoraria from Astellas Pharma. CP reports consulting or advisory fees from BMS, MSD, Pfizer, Ipsen Eusa, Eisai and General Electric; speaker fees from BMS, MSD, Pfizer, Ipsen, Eusa, Eisai, General Electric, Janssen and AstraZeneca; research funding from Pfizer; expert testimony fees from Pfizer and Eusa; and travel accommodations and expenses from Roche. TP reports consulting fees from AstraZeneca, BMS, Exelixis, Incyte, Ipsen, Merck/MSD, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Merck Serono, Astellas, Johnson & Johnson, Eisai and Roche; honoraria from AstraZeneca, BMS, Exelixis, Incyte, Ipsen, Merck/MSD, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Merck Serono, Astellas, Johnson & Johnson, Eisai and Roche; research funding (institutional) from AstraZeneca, Roche, BMS, Exelixis, Ipsen, Merck/MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Merck Serono, Astellas, Johnson & Johnson and Eisai; and travel accommodations and expenses from Roche, Pfizer, MSD, AstraZeneca and Ipsen. FD reports research funding (institutional) from MSD, Pfizer and Ipsen. SG reports research funding from Bayer, BMS, Pfizer, Novartis, Corvus, Pfizer, Acceleron, Merck, Agensys, Seattle Genetics, Calithera, Immunomedics, Corvus and Eisai; and consulting or advisory fees from Bayer, BMS, Exelixis, Corvus, Genentech, Sanofi/Genzyme, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Eisai, Merck and EMD Serono. CKK reports advisory board fees from Janssen, Astellas, Pfizer, Ipsen, Eisai, Roche, Merck and BMS; and lecture fees from Pfizer, Ipsen, Eisai and BMS. HG reports advisory board fees from Pfizer, Astellas, Ipsen, Roche and BMS. M-OG reports research funding from Novartis, BMS and Intuitive Surgical; advisory fees from Novartis, BMS, Pfizer, Bayer HealthCare, Astellas, Intuitive Surgical, AstraZeneca, MSD, Janssen Cilag, ONO Pharmaceutical, Ipsen Pharma and Merck Serono; and lecture fees from Novartis, BMS, Pfizer, Astellas, Hexal, Apogepha, AstraZeneca, MSD, ONO Pharmaceutical, Ipsen Pharma, Medac and Merck Serono. YT reports research funding from ONO Pharmaceutical, Pfizer and Takeda; consulting or advisory fees from ONO Pharmaceutical; and honoraria from ONO Pharmaceutical, BMS and Pfizer. DC reports research funding (institutional) from Janssen Oncology; consulting or advisory fees from Janssen Oncology, Roche/Genentech, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Ipsen, BMS, MSD Oncology, Bayer, Lilly, Sanofi, Pierre Fabre and Boehringer Ingelheim; and travel accommodations and expenses from Pfizer, Roche, BMS and AstraZeneca Spain. BIR reports research funding from Pfizer, Merck, GNE/Roche, Aveo, AstraZeneca and BMS; consulting fees from BMS, Pfizer, GNE/Roche, Aveo, Novartis, Synthorx, Peloton, Compugen, Merck, Arravive, Surface Oncology and 3D Medicines; and stock ownership in PTC therapeutics. TKC reports clinical trial grants from BMS, Exelixis, Pfizer, Merck, AstraZeneca, Lilly, Eisai, Novartis, GSK and EMD Serono; consulting or advisory fees from BMS, Exelixis, Pfizer, Merck, AstraZeneca, Lilly, Eisai, Novartis, GSK and EMD Serono; manuscript preparation fees from BMS, Exelixis, Pfizer, Merck, AstraZeneca, Lilly, Eisai, Novartis, GSK and EMD Serono; travel accommodations and expenses from BMS, Exelixis, Pfizer, Merck, AstraZeneca, Lilly, Eisai, Novartis, GSK and EMD Serono; and patent related to biomarkers of immune-oncology and cfmethDNA pending. SSS is an employee of and has stock ownership in BMS. MBM is an employee of and has stock ownership in BMS. RJM reports research funding (institutional) from Pfizer, Novartis, Eisai, Genentech, Roche and BMS; and consulting or advisory fees from Pfizer, Novartis, Eisai, Exelixis, Merck, Genentech, Incyte, Lilly, Roche and BMS.
Figures
Comment in
-
Dual immune checkpoint inhibition in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Editorial re.: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib for first-line treatment of advanced RCC: extended 4-year follow-up of the phase III CheckMate 214 trial.ESMO Open. 2021 Feb;6(1):100035. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2020.100035. Epub 2021 Jan 7. ESMO Open. 2021. PMID: 33421736 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF, et al. Survival outcomes and independent response assessment with nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: 42-month follow-up of a randomized phase 3 clinical trial. J Immunother Cancer 2020;8:e000891. 10.1136/jitc-2020-000891 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Rini BI, McDermott DF, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended follow-up of efficacy and safety results from a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2019;20:1370–85. 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30413-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

