Plasma N-terminal tau fragment levels predict future cognitive decline and neurodegeneration in healthy elderly individuals
- PMID: 33247134
- PMCID: PMC7695712
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19543-w
Plasma N-terminal tau fragment levels predict future cognitive decline and neurodegeneration in healthy elderly individuals
Abstract
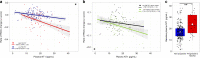
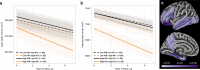
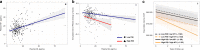
The availability of blood-based assays detecting Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology should greatly accelerate AD therapeutic development and improve clinical care. This is especially true for markers that capture the risk of decline in pre-symptomatic stages of AD, as this would allow one to focus interventions on participants maximally at risk and at a stage prior to widespread synapse loss and neurodegeneration. Here we quantify plasma concentrations of an N-terminal fragment of tau (NT1) in a large, well-characterized cohort of clinically normal elderly who were followed longitudinally. Plasma NT1 levels at study entry (when all participants were unimpaired) were highly predictive of future cognitive decline, pathological tau accumulation, neurodegeneration, and transition to a diagnosis of MCI/AD. These predictive effects were particularly strong in participants with even modestly elevated brain β-amyloid burden at study entry, suggesting plasma NT1 levels capture very early cognitive, pathologic and neurodegenerative changes along the AD trajectory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests with regards to the content or interpretation of the data in the present study. Dr. Chhatwal has served on a medical advisory board for Otsuka Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Schultz has served on medical advisory boards for Janssen Pharmaceuticals and Biogen. Drs Sperling and Johnson are involved in public–private partnership clinical trials sponsored by the NIH and Eli Lilly and Co., who owns the distribution rights to Flortaucipir (AV-1451), but they do not have any personal financial relationship with Eli Lilly. Dr. Selkoe is a director and consultant for Prothena Biosciences.
Figures


References
-
- Sperling RA, et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011;7:280–292. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

