Dynamic changes in anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies during SARS-CoV-2 infection and recovery from COVID-19
- PMID: 33247152
- PMCID: PMC7699636
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19943-y
Dynamic changes in anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies during SARS-CoV-2 infection and recovery from COVID-19
Abstract
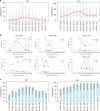
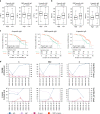
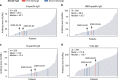
Deciphering the dynamic changes in antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 is essential for understanding the immune response in COVID-19 patients. Here we analyze the laboratory findings of 1,850 patients to describe the dynamic changes of the total antibody, spike protein (S)-, receptor-binding domain (RBD)-, and nucleoprotein (N)-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) and G (IgG) levels during SARS-CoV-2 infection and recovery. The generation of S-, RBD-, and N-specific IgG occurs one week later in patients with severe/critical COVID-19 compared to patients with mild/moderate disease, while S- and RBD-specific IgG levels are 1.5-fold higher in severe/critical patients during hospitalization. The RBD-specific IgG levels are 4-fold higher in older patients than in younger patients during hospitalization. In addition, the S- and RBD-specific IgG levels are 2-fold higher in the recovered patients who are SARS-CoV-2 RNA negative than those who are RNA positive. Lower S-, RBD-, and N-specific IgG levels are associated with a lower lymphocyte percentage, higher neutrophil percentage, and a longer duration of viral shedding. Patients with low antibody levels on discharge might thereby have a high chance of being tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 RNA after recovery. Our study provides important information for COVID-19 diagnosis, treatment, and vaccine development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Wu, Z. & McGoogan, J. M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the chinese center for disease control and prevention. J. Am. Med. Assoc.323, 1239–1242 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

