Risk factors prediction, clinical outcomes, and mortality in COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 33247599
- PMCID: PMC7753243
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.26699
Risk factors prediction, clinical outcomes, and mortality in COVID-19 patients
Abstract
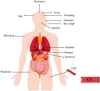
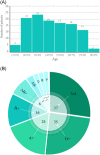
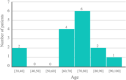
Preventing communicable diseases requires understanding the spread, epidemiology, clinical features, progression, and prognosis of the disease. Early identification of risk factors and clinical outcomes might help in identifying critically ill patients, providing appropriate treatment, and preventing mortality. We conducted a prospective study in patients with flu-like symptoms referred to the imaging department of a tertiary hospital in Iran between March 3, 2020, and April 8, 2020. Patients with COVID-19 were followed up after two months to check their health condition. The categorical data between groups were analyzed by Fisher's exact test and continuous data by Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Three hundred and nineteen patients (mean age 45.48 ± 18.50 years, 177 women) were enrolled. Fever, dyspnea, weakness, shivering, C-reactive protein, fatigue, dry cough, anorexia, anosmia, ageusia, dizziness, sweating, and age were the most important symptoms of COVID-19 infection. Traveling in the past 3 months, asthma, taking corticosteroids, liver disease, rheumatological disease, cough with sputum, eczema, conjunctivitis, tobacco use, and chest pain did not show any relationship with COVID-19. To the best of our knowledge, a number of factors associated with mortality due to COVID-19 have been investigated for the first time in this study. Our results might be helpful in early prediction and risk reduction of mortality in patients infected with COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; effective features on prediction; effective features on the mortality; risk factors.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) situation report—114. 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novelcoronavirus-2019/situation...
-
- Yan L, Zhang H‐T, Goncalves J, et al. A machine learning‐based model for survival prediction in patients with severe COVID‐19 infection. MedRxiv. 2020;1–25. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.27.20028027v3.full.pdf+html - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous