Effects of Quinacrine on Expression of Hippo signaling Pathway Components (LATS1, LATS2, and YAP) in Human Breast Cancer Stem Cells
- PMID: 33247672
- PMCID: PMC8033116
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.11.3171
Effects of Quinacrine on Expression of Hippo signaling Pathway Components (LATS1, LATS2, and YAP) in Human Breast Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
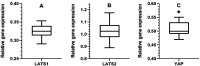
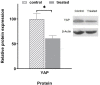
Objective: The Hippo signaling pathway has important role in the pathogenesis of some tumors. Breast cancer is the most prevalent cancer among females in the world. In recent years, various articles referred to inhibiting effect of quinacrine, a derivative of 9-aminoacridine, on the growth of several types of cancer cells. In this study, we evaluated the effect of quinacrine on expression of LATS1, LATS2, and YAP genes of the Hippo signaling pathway and YAP level in human breast cancer stem cells (MDA-MB 231 cell line). This cell line of breast cancer expresses the triple negative characteristics.
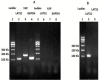
Methods: MDA-MB 231 cells was treated with 0.5 µM of quinacrine for 3 days. The dose was selected using MTT assays. The expression of genes was quantified by Real-time PCR. The protein expression was performed by Western blotting. Significance of observations were checked by means of Mann-Whitney test using p.
Keywords: Cancer stem cells; Hippo signaling pathway; MDA-MB 231; quinacrine; triple negative breast cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Alipour S, Omranipour R, Jahanzad I, et al. Very young breast cancer in a referral center in Tehran, Iran: Review of 55 Cases Aged 25 or Less throughout 33 Years. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:6529–32. - PubMed
-
- Cordenonsi M, Zanconato F, Azzolin L, et al. The Hippo transducer TAZ confers cancer stem cell-related traits on breast cancer cells. Cell. 2011;147:759–72. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

