SARS-CoV-2-Specific Neutralizing Antibody Responses in Norwegian Health Care Workers After the First Wave of COVID-19 Pandemic: A Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 33247924
- PMCID: PMC7798943
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa737
SARS-CoV-2-Specific Neutralizing Antibody Responses in Norwegian Health Care Workers After the First Wave of COVID-19 Pandemic: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: During the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, many countries experienced infection in health care workers (HCW) due to overburdened health care systems. Whether infected HCW acquire protective immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is unclear.
Methods: In a Norwegian prospective cohort study, we enrolled 607 HCW before and after the first COVID-19 wave. Exposure history, COVID-19-like symptoms, and serum samples were collected. SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies were characterized by spike-protein IgG/IgM/IgA enzyme-linked immunosorbent and live-virus neutralization assays.
Results: Spike-specific IgG/IgM/IgA antibodies increased after the first wave in HCW with, but not in HCW without, COVID-19 patient exposure. Thirty-two HCW (5.3%) had spike-specific antibodies (11 seroconverted with ≥4-fold increase, 21 were seropositive at baseline). Neutralizing antibodies were found in 11 HCW that seroconverted, of whom 4 (36.4%) were asymptomatic. Ninety-seven HCW were tested by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) during follow-up; 8 were positive (7 seroconverted, 1 had undetectable antibodies).
Conclusions: We found increases in SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies in infected HCW, especially after COVID-19 patient exposure. Our data show a low number of SARS-CoV-2-seropositive HCW in a low-prevalence setting; however, the proportion of seropositivity was higher than RT-PCR positivity, highlighting the importance of antibody testing.
Keywords: COVID-19; IgA; IgG; IgM; SARS-CoV-2; antibody characterization; health care workers; neutralizing antibody; seroconversion; spike protein.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
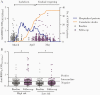
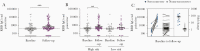

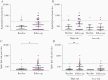

Comment in
-
SARS-CoV-2 in health and care staff in Norway, 2020.Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2021 Feb 9;141(3). doi: 10.4045/tidsskr.20.1048. Print 2021 Feb 23. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2021. PMID: 33624971 English, Norwegian.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Timeline of WHO’s response to COVID-19 https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/29-06-2020-covidtimeline. Accessed 30 July 2020.
-
- Livingston E, Bucher K. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Italy. JAMA 2020; 323:1335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

