Insulin Treatment Is Associated with Increased Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 and Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 33248471
- PMCID: PMC7682421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.014
Insulin Treatment Is Associated with Increased Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 and Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
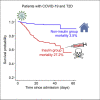
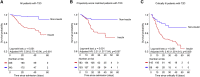
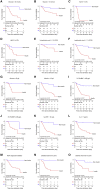
COVID-19 caused by SARS-COV-2 infection can lead to multi-organ injuries and significant mortality in severe and critical patients, especially among those individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) as a comorbidity. While attenuated mortality was observed with aggressive glucose control, it was unclear whether therapeutic regimens including insulin treatment were beneficial for patients with COVID-19 and T2D. This retrospective study investigated 689 patients with COVID-19 and T2D from a cohort of 3,305 cases from Wuhan, China. Unexpectedly, we found that insulin treatment for patients with COVID-19 and T2D was associated with a significant increase in mortality (27.2% versus 3.5%; adjusted HR, 5.38 [2.75-10.54]). Further analysis showed that insulin treatment was associated with enhanced systemic inflammation and aggravated injuries of vital organs. Therefore, insulin treatment for patients with COVID-19 and T2D should be used with caution.
Keywords: COVID-19; antidiabetic treatment; glycemic control; inflammation; insulin; mortality; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Brundage S.I., Kirilcuk N.N., Lam J.C., Spain D.A., Zautke N.A. Insulin increases the release of proinflammatory mediators. J. Trauma. 2008;65:367–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

