Cost-Effectiveness of Testing and Treatment for Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus Infections: An Analysis by Scenarios, Regions, and Income
- PMID: 33248510
- PMCID: PMC7806510
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jval.2020.06.015
Cost-Effectiveness of Testing and Treatment for Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus Infections: An Analysis by Scenarios, Regions, and Income
Abstract
Objectives: Testing and treatment for hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection are highly effective, high-impact interventions. This article aims to estimate the cost-effectiveness of scaling up these interventions by scenarios, regions, and income groups.
Methods: We modeled costs and impacts of hepatitis elimination in 67 low- and middle-income countries from 2016 to 2030. Costs included testing and treatment commodities, healthcare consultations, and future savings from cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinomas averted. We modeled disease progression to estimate disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) averted. We estimated incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) by regions and World Bank income groups, according to 3 scenarios: flatline (status quo), progress (testing/treatment according to World Health Organization guidelines), and ambitious (elimination).
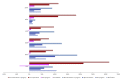
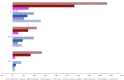
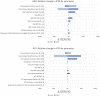
Results: Compared with no action, current levels of testing and treatment had an ICER of $807/DALY for HBV and -$62/DALY (cost-saving) for HCV. Scaling up to progress scenario, both interventions had ICERs less than the average gross domestic product/capita of countries (HBV: $532/DALY; HCV: $613/DALY). Scaling up from flatline to elimination led to higher ICERs across countries (HBV: $927/DALY; HCV: $2528/DALY, respectively) that remained lower than the average gross domestic product/capita. Sensitivity analysis indicated discount rates and commodity costs were main factors driving results.
Conclusions: Scaling up testing and treatment for HBV and HCV infection as per World Health Organization guidelines is a cost-effective intervention. Elimination leads to a much larger impact though ICERs are higher. Price reduction strategies are needed to achieve elimination given the substantial budget impact at current commodity prices.
Keywords: DALY; cost-effectiveness; elimination; viral hepatitis.
Copyright © 2020 World Health Organization. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Global hepatitis report, 2017. World Health Organization. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/255016/1/9789241565455-eng.pdf?...
-
- Global health sector strategy on viral hepatitis, 2016–2021 – towards ending hepatitis. World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/246177/WHO-HIV-2016.06-...
-
- World Health Organization Progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections 2019. Accountability for the global health sector strategies, 2016–2021. https://www.who.int/hiv/strategy2016-2021/progress-report-2019/en/
-
- Guidelines on hepatitis B and C testing. World Health Organization. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/254621/1/9789241549981-eng.pdf?...
-
- Guidelines for the prevention, care and treatment of persons with chronic hepatitis B infection. World Health Organization. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/154590/1/9789241549059_eng.pdf?... - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

