Increased CD4 : CD8 ratio normalization with implementation of current ART management guidelines
- PMID: 33249444
- PMCID: PMC7879150
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkaa484
Increased CD4 : CD8 ratio normalization with implementation of current ART management guidelines
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the time to CD4 : CD8 ratio normalization among Canadian adults living with HIV in the modern ART era. To identify characteristics associated with ratio normalization.
Patients and methods: Retrospective analysis of the Canadian Observational Cohort (CANOC), an interprovincial cohort of ART-naive adults living with HIV, recruited from 11 treatment centres across Canada. We studied participants initiating ART between 1 January 2011 and 31 December 2016 with baseline CD4 : CD8 ratio <1.0 and ≥2 follow-up measurements. Normalization was defined as two consecutive CD4 : CD8 ratios ≥1.0. Kaplan-Meier estimates and log-rank tests described time to normalization. Univariable and multivariable proportional hazards (PH) models identified factors associated with ratio normalization.
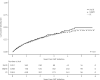
Results: Among 3218 participants, 909 (28%) normalized during a median 2.6 years of follow-up. Participants with higher baseline CD4+ T-cell count were more likely to achieve normalization; the probability of normalization by 5 years was 0.68 (95% CI 0.62-0.74) for those with baseline CD4+ T-cell count >500 cells/mm3 compared with 0.16 (95% CI 0.11-0.21) for those with ≤200 cells/mm3 (P < 0.0001). In a multivariable PH model, baseline CD4+ T-cell count was associated with a higher likelihood of achieving ratio normalization (adjusted HR = 1.5, 95% CI 1.5-1.6 per 100 cells/mm3, P < 0.0001). After adjusting for baseline characteristics, time-dependent ART class was not associated with ratio normalization.
Conclusions: Early ART initiation, at higher baseline CD4+ T-cell counts, has the greatest impact on CD4 : CD8 ratio normalization. Our study supports current treatment guidelines recommending immediate ART start, with no difference in ratio normalization observed based on ART class used.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Serrano-Villar S, Sainz T, Lee SA. et al. HIV-infected individuals with low CD4/CD8 ratio despite effective antiretroviral therapy exhibit altered T cell subsets, heightened CD8+ T cell activation, and increased risk of non-AIDS morbidity and mortality. PLoS Pathog 2014; 10: e1004078. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Serrano-Villar S, Gutierrez C, Vallejo A. et al. The CD4/CD8 ratio in HIV-infected subjects is independently associated with T-cell activation despite long-term viral suppression. J Infect 2013; 66: 57–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials