Activation of Preoptic Arginine Vasopressin Neurons Induces Hyperthermia in Male Mice
- PMID: 33249461
- PMCID: PMC7758908
- DOI: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa217
Activation of Preoptic Arginine Vasopressin Neurons Induces Hyperthermia in Male Mice
Abstract
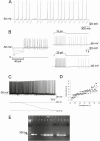
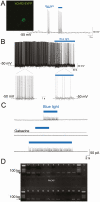
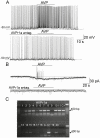
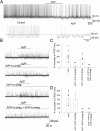
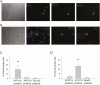
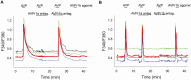
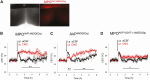
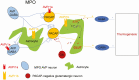
Arginine vasopressin (AVP) is a neuropeptide acting as a neuromodulator in the brain and plays multiple roles, including a thermoregulatory one. However, the cellular mechanisms of action are not fully understood. Carried out are patch clamp recordings and calcium imaging combined with pharmacological tools and single-cell RT-PCR to dissect the signaling mechanisms activated by AVP. Optogenetics combined with patch-clamp recordings were used to determine the neurochemical nature of these neurons. Also used is telemetry combined with chemogenetics to study the effect of activation of AVP neurons in thermoregulatory mechanisms. This article reports that AVP neurons in the medial preoptic (MPO) area release GABA and display thermosensitive firing activity. Their optogenetic stimulation results in a decrease of the firing rates of MPO pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) neurons. Local application of AVP potently modulates the synaptic inputs of PACAP neurons, by activating neuronal AVPr1a receptors and astrocytic AVPr1b receptors. Chemogenetic activation of MPO AVP neurons induces hyperthermia. Chemogenetic activation of all AVP neurons in the brain similarly induces hyperthermia and, in addition, decreases the endotoxin activated fever as well as the stress-induced hyperthermia.
Keywords: AVPr1a receptor; AVPr1b receptor; arginine vasopressin; hyperthermia; medial preoptic area.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



References
-
- Hoffman GE, McDonald T, Figueroa JP, Nathanielsz PW. Neuropeptide cells and fibers in the hypothalamus and pituitary of the fetal sheep: comparison of oxytocin and arginine vasopressin. Neuroendocrinology. 1989;50(6):633-643. - PubMed
-
- Ueta Y, Dayanithi G, Fujihara H. Hypothalamic vasopressin response to stress and various physiological stimuli: visualization in transgenic animal models. Horm Behav. 2011;59(2):221-226. - PubMed
-
- Richard P, Moos F, Dayanithi G, Gouzènes L, Sabatier N. Rhythmic activities of hypothalamic magnocellular neurons: autocontrol mechanisms. Biol Cell. 1997;89(9):555-560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

