Molecular forms of neurogranin in cerebrospinal fluid
- PMID: 33249594
- PMCID: PMC8378242
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.15252
Molecular forms of neurogranin in cerebrospinal fluid
Abstract
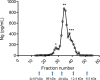
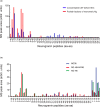
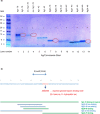
Neurogranin (Ng) is a 78 amino acid neuronal protein and a biomarker candidate for Alzheimer's disease (AD). Ng has been suggested to bind to calmodulin and phosphatidic acid via its centrally located IQ domain. Ng is cleaved within this functionally important domain, yielding the majority of fragments identified in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), suggesting that cleavage of Ng may be a mechanism to regulate its function. Up to now, Ng has been shown to be present in CSF as both C-terminal fragments as well as full-length protein. To obtain an overview of the different molecular forms of Ng present in CSF, we show by size exclusion chromatography (SEC), immunoblotting, immunoprecipitation, and MS that Ng is present in CSF as several molecular forms. Besides monomeric full-length Ng, also higher molecular weight forms of Ng, and C-terminal- and previously not identified N-terminal fragments were observed. We found by immunodepletion that C-terminal peptides contribute on average to ~50% of the total-Ng ELISA signal in CSF samples. There were no differences in the overall C-terminal fragment/total-Ng ratios between samples from AD and control groups. In addition, we found that monomeric Ng and its C-terminal fragments bind to heparin via a heparin-binding motif, which might be of relevance for their export mechanism from neurons. Taken together, this study highlights the presence of several molecular forms of Ng in CSF, comprising monomeric full-length Ng, and N- and C-terminal truncations of Ng, as well as larger forms of still unknown composition.
Keywords: CSF; heparin-binding motif; neurogranin.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Neurochemistry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International Society for Neurochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
HZ has served at advisory boards of Denali, Roche Diagnostics, Samumed, CogRx and Wave, has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Fujirebio, Alzecure and Biogen, and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB, a GU Ventures‐based platform company at the University of Gothenburg. KB has served as a consultant or at advisory boards for Alzheon, Abcam, Axon, Biogen, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche Diagnostics, and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB, a GU Ventures‐based platform company at the University of Gothenburg. The other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Alzoubi, K. H., Gerges, N. Z., & Alkadhi, K. A. (2005). Levothyroxin restores hypothyroidism‐induced impairment of LTP of hippocampal CA1: electrophysiological and molecular studies. Experimental Neurology, 195(2), 330–341. - PubMed
-
- Baudier, J., Deloulme, J. C., Alain Van Dorsselaer, A. V., Black, D., & Matthes, H. W. D. (1991). Purification and Characterization of a brain specific Protein Kinase C Substrate, Neurogranin (p 17). The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 266, 229–237. - PubMed
-
- Becker, B., Nazir, F. H., Brinkmalm, G., Camporesi, E., Kvartsberg, H., Portelius, E., Boström, M., Kalm, M., Höglund, K., Olsson, M., Zetterberg, H., & Blennow, K. (2018). Alzheimer‐associated cerebrospinal fluid fragments of neurogranin are generated by Calpain‐1 and prolyl endopeptidase. Molecular Neurodegeneration, 13, 47. 10.1186/s13024-018-0279-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

