The neck-shaft angle is the key factor for the positioning of calcar screw when treating proximal humeral fractures with a locking plate
- PMID: 33249912
- PMCID: PMC7954146
- DOI: 10.1302/0301-620X.102B12.BJJ-2020-0070.R1
The neck-shaft angle is the key factor for the positioning of calcar screw when treating proximal humeral fractures with a locking plate
Abstract
Aims: The aim of this study was to explore why some calcar screws are malpositioned when a proximal humeral fracture is treated by internal fixation with a locking plate, and to identify risk factors for this phenomenon. Some suggestions can be made of ways to avoid this error.
Methods: We retrospectively identified all proximal humeral fractures treated in our institution between October 2016 and October 2018 using the hospital information system. The patients' medical and radiological data were collected, and we divided potential risk factors into two groups: preoperative factors and intraoperative factors. Preoperative factors included age, sex, height, weight, body mass index, proximal humeral bone mineral density, type of fracture, the condition of the medial hinge, and medial metaphyseal head extension. Intraoperative factors included the grade of surgeon, neck-shaft angle after reduction, humeral head height, restoration of medial support, and quality of reduction. Adjusted binary logistic regression and multivariate logistic regression models were used to identify pre- and intraoperative risk factors. Area under the curve (AUC) analysis was used to evaluate the discriminative ability of the multivariable model.
Results: Data from 203 patients (63 males and 140 females) with a mean age of 62 years (22 to 89) were analyzed. In 49 fractures, the calcar screw was considered to be malpositioned; in 154 it was in the optimal position. The rate of malpositioning was therefore 24% (49/203). No preoperative risk factor was found for malpositioning of the calcar screws. Only the neck-shaft angle was found to be related to the risk of screw malpositioning in a multivariate model (with an AUC of 0.72). For the fractures in which the neck-shaft angle was reduced to between 130° and 150°, 91% (133/46) of calcar screws were in the optimal position.
Conclusion: The neck-shaft angle is the key factor for the appropriate positioning of calcar screws when treating a proximal humeral fracture with a locking plate. We recommend reducing the angle to between 130° and 150°. Cite this article: Bone Joint J 2020;102-B(12):1629-1635.
Keywords: Calcar screw; Neck-shaft angle; Proximal humeral fracture; Surgery.
Figures

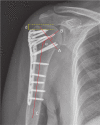
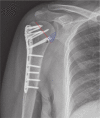


References
-
- Gardner MJ, Weil Y, Barker JU, Kelly BT, Helfet DL, Lorich DG. The importance of medial support in locked plating of proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21(3):185–191. - PubMed
-
- Cha H, Park K-B, Oh S, Jeong J. Treatment of comminuted proximal humeral fractures using locking plate with strut allograft. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(5):781–785. - PubMed
-
- Panchal K, Jeong J-J, Park S-E, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes of unstable proximal humeral fractures treated with a locking plate and fibular strut allograft. Int Orthop. 2016;40(3):569–577. - PubMed
-
- Schliemann B, Wähnert D, Theisen C, et al. How to enhance the stability of locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures? an overview of current biomechanical and clinical data. Injury. 2015;46(7):1207–1214. - PubMed

