Anemia in Diabetic Patients Reflects Severe Tubulointerstitial Injury and Aids in Clinically Predicting a Diagnosis of Diabetic Nephropathy
- PMID: 33250462
- PMCID: PMC8170246
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.5455-20
Anemia in Diabetic Patients Reflects Severe Tubulointerstitial Injury and Aids in Clinically Predicting a Diagnosis of Diabetic Nephropathy
Abstract
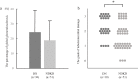
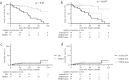
Objective A kidney biopsy is generally performed in diabetic patients to discriminate between diabetic nephropathy (DN) and non-diabetic kidney disease (NDKD) and to provide more specific treatments. This study investigated the impact of anemia on the renal pathology and the clinical course in patients who underwent a kidney biopsy. Methods We reviewed 81 patients with type 2 diabetes who underwent a percutaneous kidney biopsy. Patients were classified into two groups: isolated DN (DN group, n=30) and NDKD alone or concurrent DN (NDKD group, n=51) groups. The laboratory and pathological findings and clinical courses were investigated. Results In the NDKD group, membranous nephropathy was the most common finding (23.5%), followed by IgA nephropathy (17.6%) and crescentic glomerulonephritis (13.7%). In the logistic regression analysis, the absence of severe hematuria and presence of anemia were significantly associated with a diagnosis of DN. Akaike's information criterion (AIC) and net reclassification improvement (NRI) analyses revealed improved predictive performance by adding anemia to the conventional factors (AIC 100.152 to 91.844; NRI 27.0%). The tissues of patients in the DN group demonstrated more severe interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IF/TA) than those in the NDKD group (p<0.05) regardless of the rate of global glomerulosclerosis, and IF/TA was related to the prevalence of anemia (odds ratio: 7.31, 95% confidence interval: 2.33-23.00, p<0.01) according to a multivariable regression analysis. Furthermore, the isolated DN group demonstrated a poorer prognosis than the NDKD group. Conclusion DN is associated with anemia because of severe IF/TA regardless of the renal function, and anemia helps clinician discriminate clinically between isolated DN and NDKD.
Keywords: interstitial fibrosis; non-diabetic renal diseases; percutaneous kidney biopsy; renal anemia; retinopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Nitta K, Masakane I, Hanafusa N, et al. . 2018 Annual Dialysis Data Report, JSDT Renal Data Registry. Nihon Toseki Igakkai Zasshi (Jpn J Dial Ther) 52: 679-754, 2019(in Japanese, Abstract in English).
-
- Soni SS, Gowrishankar S, Kishan AG, Raman A. Non diabetic renal disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nephrology (Carlton) 11: 533-537, 2006. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

