Characteristics of suboptimal immune response after initiating antiretroviral therapy among people living with HIV with a pre-treatment CD4 T cell count <200 cells/mm3 in Thailand
- PMID: 33251023
- PMCID: PMC7646671
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jve.2020.100005
Characteristics of suboptimal immune response after initiating antiretroviral therapy among people living with HIV with a pre-treatment CD4 T cell count <200 cells/mm3 in Thailand
Abstract
Background: Complete recovery of the CD4 T cell count is uncommon among chronically HIV-infected individuals with very low pre-treatment CD4 count. We studied the prevalence of chronically immune recovery and its associated factors including immune characteristics chronic HIV-infected Thais.
Methods: Treatment-naïve participants (n = 375) from the HIV-NAT 006 cohort with a pre-treatment CD4 T cell count after initiating antiretroviral therapy (ART) and having achieved a suppressed viremia (HIV-RNA level < 400 copies/mL) were retrospectively followed at the Thai Red Cross AIDS Research Centre, Bangkok, Thailand. Suboptimal immune recovery (SIR) was defined as having a CD4+ T cell count <200 cells/mm3 for 3 years after ART initiation. A case-control sub-study matched for age, sex and pre-ART CD4 T cell count was conducted to compare immunological characteristics between SIR (n = 17) and non-SIR (n = 24) participants. Immunological biomarkers such as interleukin-7 (IL-7) and soluble CD14 (sCD14) and other covariates including cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA level, baseline hemoglobin level, hepatitis B and C co-infections, and T cell subsets associated with immune activation and exhaustion were evaluated.
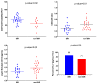
Results: Among 375 participants with pre-ART CD4 T cell counts < 200 cells/mm3, the prevalence of SIR was 39.7%, 19.7% and 7.7% at years 1, 2 and 3 after starting ART, respectively. In a multivariate analysis, a pre-ART CD4 T cell count ≤100 cells/mm3 (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 9.45, 95% CI 2.92-30.61, p < 0.001), older age (aOR 1.07, 95% CI 1.01-1.13, p = 0.029) and baseline HIV-RNA level (aOR 0.36, 95% CI 0.21-0.59, p < 0.001) were independently associated with SIR at year 3 after ART initiation. In the matched case-control sub-study (cases = 17, controls = 24), there was a higher prevalence of hepatitis C co-infection (18.8% vs. 0%, p = 0.05), lower sCD14 levels (mean, 6.23 vs. 6.27 log10 pg/mL, p = 0.04), lower CD8 T cell counts (mean, 514 vs. 876, p = 0.0003), lower CD4/CD8 T cell ratio (mean, 0.27 vs. 0.41, p = 0.01) and higher expression of PD1 on CD8+ T cells (74.2% vs. 65.1%, p = 0.02) observed in SIR participants compared to their non-SIR counterparts at year 3 after ART initiation.
Conclusions: Nearly 10% of the study participants who had achieved virological suppression failed to recover a CD4 T cell count > 200 cells/mm3 after 3 years of ART which was with a very low pre-ART CD4 T cell count and older age. The long-term clinical outcomes of SIR participants need to be further explored.
Keywords: Antiretroviral treatment; Asian; Immune characteristics; Suboptimal immune recovery.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
AA has received honorarium for consultation from ViiV Healthcare. KR received honoraria or consultation fees from Merck, Roche, Jensen-Cilag, Johnson & Johnson, Mylan and GPO (Governmental pharmaceutical organization, Thailand); has participated in a company sponsored speaker’s bureau from Abbott, Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Roche, Jensen-Cilag, ViiV Healthcare, and GPO (Governmental pharmaceutical organization); and received Chulalongkorn Academic Advancement into Its 2nd Century Project (CUAASC). JA has received honoraria for participating in advisory meetings from ViIV Healthcare, Merck, Gilead, Roche and AbbVie. The rest of the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Klatzmann D., Barre-Sinoussi F., Nugeyre M.T., Danquet C., Vilmer E., Griscelli C. Selective tropism of lymphadenopathy associated virus (LAV) for helper-inducer T lymphocytes. Science. 1984;225(4657):59–63. - PubMed
-
- Masur H., Ognibene F.P., Yarchoan R., Shelhamer J.H., Baird B.F., Travis W. CD4 counts as predictors of opportunistic pneumonias in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Ann. Intern. Med. 1989;111(3):223–231. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

