Clear cell renal cell carcinoma detection by multimodal photoacoustic tomography
- PMID: 33251109
- PMCID: PMC7683266
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pacs.2020.100221
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma detection by multimodal photoacoustic tomography
Abstract
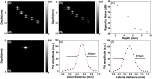
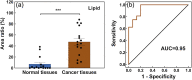
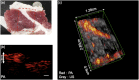
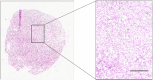
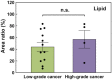
There is a need for accurate and rapid detection of renal cancer in clinic. Here, we integrated photoacoustic tomography (PAT) with ultrasound imaging in a single system, which achieved tissue imaging depth about 3 mm and imaging speed about 3.5 cm2/min. We used the wavelength at 1197 nm to map lipid distribution in normal renal tissues and clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) tissues collected from 19 patients undergone nephrectomy. Our results indicated that the photoacoustic signal from lipids was significantly higher in ccRCC tissues than that in normal tissues. Moreover, based on the quantification of lipid area ratio, we were able to differentiate normal and ccRCC with 100 % sensitivity, 80 % specificity, and area under receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.95. Our findings demonstrate that multimodal PAT can differentiate normal and ccRCC by integrating the morphologic information from ultrasound and lipid amount information from vibrational PAT.
Keywords: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma; Lipid accumulation; Photoacoustic tomography.
© 2020 Beihang University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Becker A., Pradel L., Kluth L., Schmid M., Eichelberg C., Ahyai S., Trinh Q., Seiler D., Dahlem R., Hansen J. Laparoscopic versus open partial nephrectomy for clinical T1 renal masses: no impact of surgical approach on perioperative complications and long-term postoperative quality of life. World J. Urol. 2015;33:421–426. doi: 10.1007/s00345-014-1318-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bensalah K., Pantuck A.J., Rioux-Leclercq N., Thuret R., Montorsi F., Karakiewicz P.I., Mottet N., Zini L., Bertini R., Salomon L., Villers A., Soulie M., Bellec L., Rischmann P., De La Taille A., Avakian R., Crepel M., Ferriere J.M., Bernhard J.C., Dujardin T., Pouliot F., Rigaud J., Pfister C., Albouy B., Guy L., Joniau S., van Poppel H., Lebret T., Culty T., Saint F., Zisman A., Raz O., Lang H., Spie R., Wille A., Roigas J., Aguilera A., Rambeaud B., Piñeiro L.M., Nativ O., Farfara R., Richard F., Roupret M., Doehn C., Bastian P.J., Muller S.C., Tostain J., Belldegrun A.S., Patard J.J. Positive surgical margin appears to have negligible impact on survival of renal cell carcinomas treated by nephron-sparing surgery. Eur. Urol. 2010;57:466–471. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.03.048. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Breda A., Stepanian S.V., Liao J., Lam J.S., Guazzoni G., Stifelman M., Perry K., Celia A., Breda G., Fornara P., Jackman S., Rosales A., Palou J., Grasso M., Pansadoro V., Disanto V., Porpiglia F., Milani C., Abbou C., Gaston R., Janetschek G., Soomro N.A., de la Rosette J., Laguna M.P., Schulam P.G. Positive margins in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy in 855 cases: a multi-institutional survey from the United States and Europe. J. Urol. 2007;178:47–50. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2007.03.045. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

