Emerging Roles and Potential Biological Value of CircRNA in Osteosarcoma
- PMID: 33251132
- PMCID: PMC7673402
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.552236
Emerging Roles and Potential Biological Value of CircRNA in Osteosarcoma
Abstract
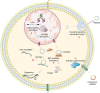
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are endogenous noncoding RNAs that are widely found in eukaryotic cells. They have been found to play a vital biological role in the development of human diseases. At present, circRNAs have been involved in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and targeted treatment of multiple tumors. This article reviews the research progress of circRNAs in osteosarcoma (OSA) in recent years. The potential connection between circRNAs and OSA cell proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis, and chemotherapy sensitivity or resistance, as well as clinical values, is described in this review. Their categories and functions are generally summarized to facilitate a better understanding of OSA pathogenesis, and findings suggest novel circRNA-based methods may be used to investigate OSA and provide an outlook for viable biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Keywords: circular RNAs; epithelial mesenchymal transition; metastasis; osteosarcoma; prognosis.
Copyright © 2020 Liu, Yang, Fu and Liu.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microarray Expression Profile and Functional Analysis of Circular RNAs in Osteosarcoma.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(3):969-985. doi: 10.1159/000481650. Epub 2017 Sep 29. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28957794
-
Emerging landscape of circular RNAs as biomarkers and pivotal regulators in osteosarcoma.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Dec;235(12):9037-9058. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29754. Epub 2020 May 26. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32452026 Review.
-
The emerging role of circular RNAs in common solid malignant tumors in children.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Jun 11;21(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01998-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34116651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive characterization of circular RNAs in osteosarcoma cell lines.Cell Signal. 2020 Jul;71:109603. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109603. Epub 2020 Mar 19. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 32199934
-
Circular RNAs: an emerging landscape in tumor metastasis.Am J Cancer Res. 2019 Apr 1;9(4):630-643. eCollection 2019. Am J Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31105992 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Silencing circOMA1 Inhibits Osteosarcoma Progression by Sponging miR-1294 to Regulate c-Myc Expression.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 13;12:889583. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.889583. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35493998 Free PMC article.
-
CircDOCK1 Regulates miR-186/DNMT3A to Promote Osteosarcoma Progression.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 23;10(12):3013. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123013. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551768 Free PMC article.
-
The Landscape of Regulatory Noncoding RNAs in Ewing's Sarcoma.Biomedicines. 2021 Jul 31;9(8):933. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9080933. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34440137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinicopathologic significance and prognostic value of circRNAs in osteosarcoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Oct 7;16(1):578. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02568-2. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34620208 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNA-CIRH1A Promotes the Development of Osteosarcoma by Regulating PI3K/AKT and JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathways.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Sep;66(9):2241-2253. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00812-0. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37608076 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

