T1 Stage Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A CT-Based Radiomics Nomogram to Estimate the Risk of Recurrence and Metastasis
- PMID: 33251142
- PMCID: PMC7672185
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.579619
T1 Stage Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A CT-Based Radiomics Nomogram to Estimate the Risk of Recurrence and Metastasis
Abstract
Objectives: To develop and validate a radiomics nomogram to improve prediction of recurrence and metastasis risk in T1 stage clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC).
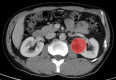
Methods: This retrospective study recruited 168 consecutive patients (mean age, 53.9 years; range, 28-76 years; 43 women) with T1 ccRCC between January 2012 and June 2019, including 50 aggressive ccRCC based on synchronous metastasis or recurrence after surgery. The patients were divided into two cohorts (training and validation) at a 7:3 ratio. Radiomics features were extracted from contrast enhanced CT images. A radiomics signature was developed based on reproducible features by means of the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator method. Demographics, laboratory variables (including sex, age, Fuhrman grade, hemoglobin, platelet, neutrophils, albumin, and calcium) and CT findings were combined to develop clinical factors model. Integrating radiomics signature and independent clinical factors, a radiomics nomogram was developed. Nomogram performance was determined by calibration, discrimination, and clinical usefulness.
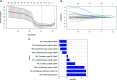
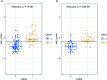
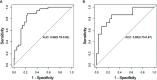
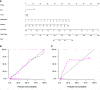
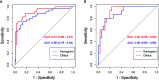
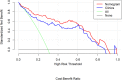
Results: Ten features were used to build radiomics signature, which yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.86 in the training cohort and 0.85 in the validation cohort. By incorporating the sex, maximum diameter, neutrophil count, albumin count, and radiomics score, a radiomics nomogram was developed. Radiomics nomogram (AUC: training, 0.91; validation, 0.92) had higher performance than clinical factors model (AUC: training, 0.86; validation, 0.90) or radiomics signature as a means of identifying patients at high risk for recurrence and metastasis. The radiomics nomogram had higher sensitivity than clinical factors mode (McNemar's chi-squared = 4.1667, p = 0.04) and a little lower specificity than clinical factors model (McNemar's chi-squared = 3.2, p = 0.07). The nomogram showed good calibration. Decision curve analysis demonstrated the superiority of the nomogram compared with the clinical factors model in terms of clinical usefulness.
Conclusion: The CT-based radiomics nomogram could help in predicting recurrence and metastasis risk in T1 ccRCC, which might provide assistance for clinicians in tailoring precise therapy.
Keywords: clear cell renal cell carcinoma; computed tomography; neoplasm metastasis; prediction model; recurrence.
Copyright © 2020 Kang, Sun, Gu, Yang, Yuan, Ji, Huang, Yu, Duan and Wang.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and validation of A CT-based radiomics nomogram for prediction of synchronous distant metastasis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 4;12:1016583. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1016583. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36686790 Free PMC article.
-
A CT-based radiomics nomogram for differentiation of renal angiomyolipoma without visible fat from homogeneous clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Eur Radiol. 2020 Feb;30(2):1274-1284. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06427-x. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31506816
-
Development and validation of a CT-based nomogram for preoperative prediction of clear cell renal cell carcinoma grades.Eur Radiol. 2021 Aug;31(8):6078-6086. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07667-y. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33515086
-
MRI radiomics-based nomogram for individualised prediction of synchronous distant metastasis in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Eur Radiol. 2021 Feb;31(2):1029-1042. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07184-y. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 32856163
-
A Computed Tomography-Based Radiomics Nomogram to Preoperatively Predict Tumor Necrosis in Patients With Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2020 May 29;10:592. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00592. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32547934 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Radiomics nomogram based on dual-energy spectral CT imaging to diagnose low bone mineral density.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 May 6;23(1):424. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05389-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 35524240 Free PMC article.
-
A CT-based intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics nomogram for postoperative recurrence risk stratification in localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 May 16;25(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01715-z. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40380110 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
CT-Based Radiomics Nomogram for Prediction of Progression-Free Survival in Locoregionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Sep 3;13:6911-6923. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S325373. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34512030 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a CT-Based Radiomics Nomogram for Predicting Postoperative Progression-Free Survival in Stage I-III Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 27;11:742547. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.742547. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35155180 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative CT-Based Deep Learning Model for Predicting Risk Stratification in Patients With Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 17;11:750875. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.750875. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34631589 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

