Targeting Bcl-2 Proteins in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 33251145
- PMCID: PMC7674767
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.584974
Targeting Bcl-2 Proteins in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
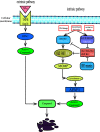
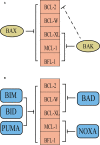
B cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) family proteins play an important role in intrinsic apoptosis. Overexpression of BCL-2 proteins in acute myeloid leukemia can circumvent resistance to apoptosis and chemotherapy. Considering this effect, the exploration of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 inhibitors is considered to have tremendous potential for the discovery of novel pharmacological modulators in cancer. This review outlines the impact of BCL-2 family proteins on intrinsic apoptosis and the development of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Furthermore, we will also review the new combination therapy with venetoclax that overcomes resistance to venetoclax and discuss biomarkers of treatment response identified in early-phase clinical trials.
Keywords: AML—acute myeloid leukemia; B cell lymphoma 2; Bcl-2 protein; intrinsic apoptosis; venetoclax (ABT-199).
Copyright © 2020 Wei, Cao, Sun, Cheng, Xiong, Jin, He, Lu and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- National Cancer Institute Surveillance Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Cancer Stat Facts: Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). Available at: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html.
-
- Tothova E, Fricova M, Stecova N, Kafkova A, Elbertova A. High expression of Bcl-2 protein in acute myeloid leukemia cells is associated with poor response to chemotherapy. Neoplasma (2002) 49(3):141–4. - PubMed
-
- Kaufmann SH, Karp JE, Svingen PA, Krajewski S, Burke PJ, Gore SD, et al. Elevated expression of the apoptotic regulator Mcl-1 at the time of leukemic relapse. Blood (1998) 91(3):991–1000. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

