CRISPR-Cas System: An Approach With Potentials for COVID-19 Diagnosis and Therapeutics
- PMID: 33251158
- PMCID: PMC7673385
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.576875
CRISPR-Cas System: An Approach With Potentials for COVID-19 Diagnosis and Therapeutics
Abstract
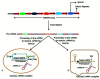
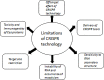
COVID-19, the human coronavirus disease caused by SARS-CoV-2, was reported for the first time in Wuhan, China in late 2019. COVID-19 has no preventive vaccine or proven standard pharmacological treatment, and consequently, the outbreak swiftly became a pandemic affecting more than 215 countries around the world. For the diagnosis of COVID-19, the only reliable diagnostics is a qPCR assay. Among other diagnostic tools, the CRISPR-Cas system is being investigated for rapid and specific diagnosis of COVID-19. The CRISPR-Cas-based methods diagnose the SARS-CoV-2 infections within an hour. Apart from its diagnostic ability, CRISPR-Cas system is also being assessed for antiviral therapy development; however, till date, no CRISPR-based therapy has been approved for human use. The Prophylactic Antiviral CRISPR in huMAN cells (PAC-MAN), which is Cas 13 based strategy, has been developed against coronavirus. Although this strategy has the potential to be developed as a therapeutic modality, it may face significant challenges for approval in human clinical trials. This review is focused on describing potential use and challenges of CRISPR-Cas based approaches for the development of rapid and accurate diagnostic technique and/or a possible therapeutic alternative for combating COVID-19. The assessment of potential risks associated with use of CRISPR will be important for future clinical advancements.
Keywords: CRISPR; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; diagnosis; pandemic (COVID-19); therapeutic.
Copyright © 2020 Kumar, Malik, Ganesh, Rahangdale, Saurabh, Natesan, Srivastava, Sharun, Yatoo, Tiwari, Singh and Dhama.
Figures


Comment in
-
Rapid identification and tracking of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern.Lancet. 2021 Apr 10;397(10282):1346-1347. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00470-0. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Lancet. 2021. PMID: 33765408 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Manipulation of genes could inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection that causes COVID-19 pandemics.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Jul;246(14):1643-1649. doi: 10.1177/15353702211008106. Epub 2021 Apr 25. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 33899542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR systems: Novel approaches for detection and combating COVID-19.Virus Res. 2021 Mar;294:198282. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198282. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Virus Res. 2021. PMID: 33428981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing CRISPR-Based Solutions for COVID-19 Diagnosis and Therapeutics.Cells. 2024 Oct 30;13(21):1794. doi: 10.3390/cells13211794. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39513901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 one year later: a retrospect of CRISPR-Cas system in combating COVID-19.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 May 13;17(8):2080-2088. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.60655. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34131407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of CRISPR/Cas system in the diagnosis of COVID-19 infection.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2021 Nov;21(11):1179-1189. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2021.1970535. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2021. PMID: 34409907 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CRISPR/Cas: a Nobel Prize award-winning precise genome editing technology for gene therapy and crop improvement.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2021 Apr 15;22(4):253-284. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2100009. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2021. PMID: 33835761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The application of CRISPR-Cas system in Staphylococcus aureus infection.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 10;10(14):e34383. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34383. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39108851 Free PMC article.
-
Role of biomaterials in the diagnosis, prevention, treatment, and study of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19).Emergent Mater. 2021;4(1):35-55. doi: 10.1007/s42247-021-00165-x. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Emergent Mater. 2021. PMID: 33748672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a rapid and ultra-sensitive RNA:DNA hybrid immunocapture based biosensor for visual detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA.PNAS Nexus. 2023 Feb 1;2(3):pgad031. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad031. eCollection 2023 Mar. PNAS Nexus. 2023. PMID: 36909823 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Diagnosis: Current and Future Techniques.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Dec 15;193(Pt B):1835-1844. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.11.016. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34774862 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

