The G-protein Coupled Receptor GPR8 Regulates Secondary Metabolism in Trichoderma reesei
- PMID: 33251193
- PMCID: PMC7676458
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.558996
The G-protein Coupled Receptor GPR8 Regulates Secondary Metabolism in Trichoderma reesei
Abstract
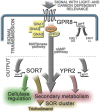
Changing environmental conditions are of utmost importance for regulation of secondary metabolism in fungi. Different environmental cues including the carbon source, light and the presence of a mating partner can lead to altered production of compounds. Thereby, the heterotrimeric G-protein pathway is of major importance for sensing and adjustment of gene regulation. Regulation of secondary metabolism is crucial in the biotechnological workhorse Trichoderma reesei for knowledge-based adjustment in industrial fermentations, but also with respect to the potential use as a host for heterologous compound production. We investigated the function of the class VII G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) gene gpr8 that is localized in the vicinity of the SOR cluster, which is responsible for biosynthesis of sorbicillinoids. GPR8 positively impacts regulation of the genes in this cluster in darkness. Accordingly, abundance of trichodimerol and dihydrotrichotetronine as well as other secondary metabolites is decreased in the deletion mutant. Transcriptome analysis moreover showed the major role of GPR8 being exerted in darkness with a considerable influence on regulation of secondary metabolism. Genes regulated in Δgpr8 overlap with those regulated directly or indirectly by the transcription factor YPR2, especially concerning genes related to secondary metabolism. The predicted FAD/FMN containing dehydrogenase gene sor7, one of the positive targets of the cascade triggered by GPR8, has a positive effect on secondary metabolite production, but also cellulase gene expression. Hence SOR7 has some overlapping, but also additional functions compared to GPR8. The G-protein coupled receptor GPR8 exerts a light dependent impact on secondary metabolism, which is in part mediated by the transcription factor YPR2 and the function of SOR7. Hence, T. reesei may apply GPR8 to adjust production of secondary metabolites and hence chemical communication to signals from the environment.
Keywords: SOR cluster; Trichoderma reesei; cellulase; chemical communication; chemosensing; heterotrimeric G-protein pathway; light response; secondary metabolism.
Copyright © 2020 Hinterdobler, Beier, Monroy, Berger, Dattenböck and Schmoll.
Figures

Similar articles
-
YPR2 is a regulator of light modulated carbon and secondary metabolism in Trichoderma reesei.BMC Genomics. 2019 Mar 13;20(1):211. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5574-8. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30866811 Free PMC article.
-
The role of PKAc1 in gene regulation and trichodimerol production in Trichoderma reesei.Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2019 Sep 10;6:12. doi: 10.1186/s40694-019-0075-8. eCollection 2019. Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31528353 Free PMC article.
-
The Kinase USK1 Regulates Cellulase Gene Expression and Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis in Trichoderma reesei.Front Microbiol. 2020 May 20;11:974. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00974. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32508786 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of plant cell wall degradation by light in Trichoderma.Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2018 Apr 24;5:10. doi: 10.1186/s40694-018-0052-7. eCollection 2018. Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29713489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tools for adapting to a complex habitat: G-protein coupled receptors in Trichoderma.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2022;193(1):65-97. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2022.06.003. Epub 2022 Jul 6. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 36357080 Review.
Cited by
-
Trichoderma - genomes and genomics as treasure troves for research towards biology, biotechnology and agriculture.Front Fungal Biol. 2022 Sep 14;3:1002161. doi: 10.3389/ffunb.2022.1002161. eCollection 2022. Front Fungal Biol. 2022. PMID: 37746224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosducin-like protein PoPlp1 impacts cellulase and amylase expression and development in Penicillium oxalicum via the G protein-cAMP signaling pathway.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 9;14:1165701. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1165701. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37362916 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular regulation of fungal secondary metabolism.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 May 20;39(8):204. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03649-6. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37209190 Review.
-
Fungal Stress Responses and the Importance of GPCRs.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Mar 11;11(3):213. doi: 10.3390/jof11030213. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular methods unravel the biosynthetic potential of Trichoderma species.RSC Adv. 2021 Jan 18;11(6):3622-3635. doi: 10.1039/d0ra09627j. eCollection 2021 Jan 14. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35424278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

