Diagnostic Value of Inflammatory Factors in Pathology of Bladder Cancer Patients
- PMID: 33251247
- PMCID: PMC7674661
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.575483
Diagnostic Value of Inflammatory Factors in Pathology of Bladder Cancer Patients
Abstract
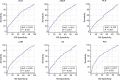
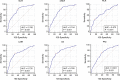
We conducted this study to evaluate the diagnostic value of Inflammatory Factors (IFs) in the pathology of bladder cancer patients. The patients who were diagnosed with urothelial bladder carcinoma (bladder cancer) and underwent surgical treatment in our center from 2014 to 2019 were enrolled. The values of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), derived Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (dNLR), Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR), Lymphocyte to Monocyte Ratio (LMR), Systemic Immune-inflammation Index (SII), and Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) were calculated by blood routine test results before operation. After obtaining the postoperative pathology of the patients, the Area Under Curve (AUC) of Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves was calculated to evaluate the diagnostic value of these IFs in pathology and their corresponding cut-off values. A total of 641 bladder cancer patients were enrolled. The median values of NLR, dNLR, PLR, LMR, SII, and PNI were 6.33, 4.09, 156.47, 2.66, 1114.29, and 51.45, respectively. Grouped patients according to the pathological grade, the NLR, dNLR, PLR, and SII of the high-grade group were significantly higher than those of the low-grade group (P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, and P < 0.001, respectively), while the LMR and PNI were significantly lower than those of the low-grade group (P = 0.003 and P < 0.001). Divided patients into non-muscle invasion group (Tis + Ta + T1) and muscle invasion group (T2 + T3 + T4), in which NLR, dNLR, PLR, and SII in the muscle invasion group were significantly higher than those in the non-muscle invasion group (P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, and P < 0.001, respectively), while LMR and PNI were significantly lower than those in the low-grade group (P = 0.012 and P < 0.001). ROC curves analyses showed that NLR, dNLR, PLR, LMR, SII, and PNI had predictive value for pathological grade (P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, and P < 0.001, respectively) and muscle invasion (P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, and P < 0.001, respectively). The results suggest the higher NLR, dNLR, PLR, SII, and lower LMR and PNI are associated with higher risk of high-grade and muscle invasive disease. However, this conclusion needs to be further clarified in the future.
Keywords: bladder cancer; derived neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; inflammatory factors; lymphocyte to monocyte ratio; neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; platelet to lymphocyte ratio; prognostic nutritional index; systemic immune-inflammation index.
Copyright © 2020 Tang, Cao, Liu, Wang, Yang and Du.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic value of preoperative inflammatory markers in patients with glioma: a multicenter cohort study.J Neurosurg. 2018 Sep;129(3):583-592. doi: 10.3171/2017.3.JNS161648. Epub 2017 Nov 3. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 29099300
-
Diagnostic and Predictive Values of Inflammatory Factors in Pathology and Survival of Patients Undergoing Total Cystectomy.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Sep 24;2020:9234067. doi: 10.1155/2020/9234067. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 33029106 Free PMC article.
-
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT DERIVED INFLAMMATORY BIOMARKERS IN PATIENTS WITH HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES.Georgian Med News. 2020 May;(302):39-44. Georgian Med News. 2020. PMID: 32672687
-
Predictive value of preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index and prognostic nutrition index in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer.J Ovarian Res. 2025 Mar 7;18(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13048-025-01631-4. J Ovarian Res. 2025. PMID: 40055764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of inflammatory markers NLR, PLR, LMR, dNLR, ANC in melanoma patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 18;15:1482746. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1482746. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39493767 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association between fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio and bone metabolism markers (β-CTX and P1NP) in Chinese individuals with osteoporotic fracture: a cross-sectional investigation.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Jan 13;26(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08276-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 39806379 Free PMC article.
-
Development and external validation of a novel nomogram model for predicting postoperative recurrence-free survival in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 15;13:1070043. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1070043. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36458001 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Value of Inflammatory and Nutritional Indexes in the Pathology of Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with Radical Cystectomy.Curr Oncol. 2023 Feb 21;30(3):2582-2597. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30030197. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36975410 Free PMC article.
-
The role of geriatric nutritional risk index in predicting survival of type B aortic dissection patients after thoracic endovascular aortic repair.J Nutr Health Aging. 2025 Jul;29(7):100572. doi: 10.1016/j.jnha.2025.100572. Epub 2025 May 14. J Nutr Health Aging. 2025. PMID: 40373393 Free PMC article.
-
Can Routine Blood and Urine Parameters Reveal Clues to Detect Bladder Cancer? A Case-Control Study.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 21;11:796975. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.796975. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35127507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giannopoulos A., Manousakas T., Gounari A., Constantinides C., Choremi-Papadopoulou H., Dimopoulos C. (2001). Comparative evaluation of the diagnostic performance of the BTA stat test, NMP22 and urinary bladder cancer antigen for primary and recurrent bladder tumors. J. Urol. 166 470–475. 10.1097/00005392-200108000-00015 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

