Randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled trial of hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin for virologic cure of non-severe Covid-19
- PMID: 33251500
- PMCID: PMC7678437
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100645
Randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled trial of hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin for virologic cure of non-severe Covid-19
Abstract
Background: Hydroxychloroquine (HC) ± azithromycin (AZ) is widely used for Covid-19. The Qatar Prospective RCT of Expediting Coronavirus Tapering (Q-PROTECT) aimed to assess virologic cure rates of HC±AZ in cases of low-acuity Covid-19.
Methods: Q-PROTECT employed a prospective, placebo-controlled design with blinded randomization to three parallel arms: placebo, oral HC (600 mg daily for one week), or oral HC plus oral AZ (500 mg day one, 250 mg daily on days two through five). At enrollment, non-hospitalized participants had mild or no symptoms and were within a day of Covid-19 positivity by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). After six days, intent-to-treat (ITT) analysis of the primary endpoint of virologic cure was assessed using binomial exact 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and χ2 testing. (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04349592, trial status closed to new participants.).
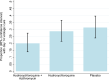
Findings: The study enrolled 456 participants (152 in each of three groups: HC+AZ, HC, placebo) between 13 April and 1 August 2020. HC+AZ, HC, and placebo groups had 6 (3·9%), 7 (4·6%), and 9 (5·9%) participants go off study medications before completing the medication course (p = 0·716). Day six PCR results were available for all 152 HC+AZ participants, 149/152 (98·0%) HC participants, and 147/152 (96·7%) placebo participants. Day six ITT analysis found no difference (p = 0·821) in groups' proportions achieving virologic cure: HC+AZ 16/152 (10·5%), HC 19/149 (12·8%), placebo 18/147 (12·2%). Day 14 assessment also showed no association (p = 0·072) between study group and viral cure: HC+AZ 30/149 (20·1%,), HC 42/146 (28·8%), placebo 45/143 (31·5%). There were no serious adverse events.
Interpretation: HC±AZ does not facilitate virologic cure in patients with mild or asymptomatic Covid-19.
Funding: The study was supported by internal institutional funds of the Hamad Medical Corporation (government health service of the State of Qatar).
Keywords: Azithromycin; Covid-19; Hyodroxychloroquine.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial or personal relationships with other people or organizations that could represent a conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ferner R.E., Aronson J.K... Hydroxychloroquine for Covid-19: what do the clinical trials tell us? 2020. https://www.cebm.net/covid-19/hydroxychloroquine-for-covid-19-what-do-th... (accessed 20 April 2020).
-
- Q-PROTECT Research Protocol. 2020. https://www.hamad.qa/EN/Hospitals-and-services/Communicable-Disease-Cent... (accessed 1 August 2020).
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous