Reduced All-Cause Mortality in the ETHOS Trial of Budesonide/Glycopyrrolate/Formoterol for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Multicenter, Parallel-Group Study
- PMID: 33252985
- PMCID: PMC7924571
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202006-2618OC
Reduced All-Cause Mortality in the ETHOS Trial of Budesonide/Glycopyrrolate/Formoterol for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Multicenter, Parallel-Group Study
Abstract
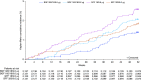
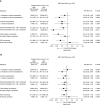
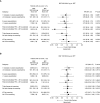
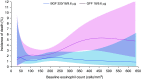
Rationale: In the phase III, 52-week ETHOS (Efficacy and Safety of Triple Therapy in Obstructive Lung Disease) trial in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (NCT02465567), triple therapy with budesonide/glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate (BGF) significantly reduced all-cause mortality compared with glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate (GFF). However, 384 of 8,509 patients were missing vital status at Week 52 in the original analyses.Objectives: To assess the robustness of the ETHOS mortality findings after additional data retrieval for patients missing Week 52 vital status in the original analyses.Methods: Patients with moderate to very severe COPD and prior history of exacerbation received twice-daily dosing with 320/18/9.6 μg of BGF (BGF 320), 160/18/9.6 μg of BGF (BGF 160), 18/9.6 μg of GFF, or 320/9.6 μg of budesonide/formoterol fumarate (BFF) (all delivered via a single metered-dose Aerosphere inhaler). Time to death (all-cause) was a prespecified secondary endpoint.Measurements and Main Results: In the final retrieved dataset, which included Week 52 vital status for 99.6% of the intent-to-treat population, risk of death with BGF 320 was significantly lower than GFF (hazard ratio, 0.51; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-0.80; unadjusted P = 0.0035). There were no significant differences in mortality when comparing BGF 320 with BFF (hazard ratio, 0.72; 95% confidence interval, 0.44-1.16; P = 0.1721), nor were significant differences observed when comparing BGF 160 against either dual comparator. Results were similar when the first 30, 60, or 90 days of treatment were excluded from the analysis. Deaths from cardiovascular causes occurred in 0.5%, 0.8%, 1.4%, and 0.5% of patients in the BGF 320, BGF 160, GFF, and BFF groups, respectively.Conclusions: Using final retrieved vital status data, triple therapy with BGF 320 reduced the risk of death compared with GFF, but was not shown to significantly reduce the risk of death compared with BFF, in patients with COPD. Triple therapy containing a lower dose of inhaled corticosteroid (BGF 160) was not shown to significantly reduce the risk of death compared with the dual therapy comparators.
Keywords: BGF metered-dose inhaler; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; inhaled corticosteroids/long-acting muscarinic antagonist/long-acting β2-agonist; mortality; triple therapy.
Figures

Comment in
-
Reigniting the TORCH: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Mortality and Inhaled Corticosteroids Revisited.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Mar 1;203(5):531-532. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202012-4300ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33326362 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to López-Campos et al. and to Rogliani and Calzetta.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Apr 1;203(7):927-928. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202012-4484LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33444510 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mortality in ETHOS: A Question of "Power".Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Apr 1;203(7):926-927. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202012-4328LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33444515 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization Global health estimates 2016: deaths by cause, age, sex, by country and by region 2000–2016 Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2018[updated 2019 Apr 11]. Available from: https://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/estimates/en/
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2020 report: global strategy for the diagnosis, management and prevention of COPD Fontana, WI: Gold Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease; 2020[updated 2020 Mar 17]. Available from: https://goldcopd.org/gold-reports/
-
- Celli B, Decramer M, Kesten S, Liu D, Mehra S, Tashkin DP UPLIFT Study Investigators. Mortality in the 4-year trial of tiotropium (UPLIFT) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180:948–955. - PubMed
-
- Calverley PMA, Anderson JA, Celli B, Ferguson GT, Jenkins C, Jones PW, et al. TORCH investigators. Salmeterol and fluticasone propionate and survival in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:775–789. - PubMed
-
- Vestbo J, Anderson JA, Brook RD, Calverley PMA, Celli BR, Crim C, et al. SUMMIT Investigators. Fluticasone furoate and vilanterol and survival in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with heightened cardiovascular risk (SUMMIT): a double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;387:1817–1826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

