Postoperative clinical outcomes and inflammatory markers after inguinal hernia repair using local, spinal, or general anesthesia: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 33253306
- PMCID: PMC7703886
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242925
Postoperative clinical outcomes and inflammatory markers after inguinal hernia repair using local, spinal, or general anesthesia: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: No consensus has yet been reached regarding the best anesthetic technique for inguinal hernia repair. This study aimed to compare postoperative clinical outcomes and inflammatory markers among patients who were anesthetized using local, spinal, or general anesthesia for inguinal hernia repair.
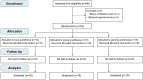
Methods: This randomized controlled trial included patients scheduled to undergo elective unilateral inguinal hernioplasty at Siriraj Hospital during November 2014 to September 2015 study period. Patients were randomly assigned to the local (LA), spinal (SA), or general (GA) anesthesia groups. Primary outcomes were postoperative pain at rest and on mobilization at 8 and 24 hours after surgery.
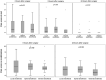
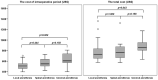
Results: Fifty-four patients were included, with 18 patients randomly assigned to each group. Patient demographic and clinical characteristics were similar among groups. There were no significant differences among groups for postoperative pain at rest or on mobilization at 8 and 24 hours after surgery. No significant differences were observed for interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and interleukin-10 at any time points in any groups. Patients with local anesthesia was associated with less time spent in anesthesia (p = 0.010) and surgery (p = 0.009), lower intraoperative cost (p = 0.003) and total cost in hospital (p = 0.036); however, patient satisfaction in the local anesthesia group (94/100) was statistically significantly lower than the spinal and general anesthesia groups (100/100) (p = 0.010).
Conclusions: No statistically significant difference was observed among groups for postoperative pain scores, duration of hospital stays, complications, or change in inflammatory markers. However, time spent in anesthesia and surgery, the intraoperative cost and total cost for hernia repair, and patient satisfaction were significantly lower in the local anesthesia group than in the other two groups.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Job CA, Fernandez MA, Dorph DJ, Betcher AM. Inguinal hernia repair. Comparison of local, epidural, and general anesthesia. N Y State J Med. 1979;79(11):1730–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

