Inorganic nanoparticles for reduction of hexavalent chromium: Physicochemical aspects
- PMID: 33254738
- PMCID: PMC7382355
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123535
Inorganic nanoparticles for reduction of hexavalent chromium: Physicochemical aspects
Abstract
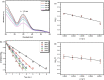
Hexavalent Chromium [Cr(VI)] is a highly carcinogenic and toxic material. It is one of the major environmental contaminants in aquatic system. Its removal from aqueous medium is a subject of current research. Various technologies like adsorption, membrane filtration, solvent extraction, coagulation, biological treatment, ion exchange and chemical reduction for removal of Cr(VI) from waste water have been developed. But chemical reduction of Cr(VI) to Cr(III) has attracted a lot of interest in the past few years because, the reduction product [Cr(III)] is one of the essential nutrients for organisms. Various nanoparticles based systems have been designed for conversion of Cr(VI) into Cr(III) which have not been critically reviewed in literature. This review present recent research progress of classification, designing and characterization of various inorganic nanoparticles reported as catalysts/reductants for rapid conversion of Cr(VI) into Cr(III) in aqueous medium. Kinetics and mechanism of nanoparticles enhanced/catalyzed reduction of Cr(VI) and factors affecting the reduction process have been discussed critically. Personal future insights have been also predicted for further development in this area.
Keywords: Chemical reduction; Hexavalent chromium; Metal nanoparticles; Nanocatalysis; Water pollution.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures







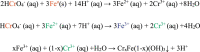



References
-
- Akram M.Y., Hameed M.U., Akhtar N., Ali S., Maitlo I., Zhu X.-Q., Jun N. Synthesis of high performance Ni3C-Ni decorated thermally expanded reduced graphene oxide (TErGO/Ni3C-Ni) nanocomposite: a stable catalyst for reduction of Cr (VI) and organic dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019;366:723–731. - PubMed
-
- Ali I., Gupta V. Advances in water treatment by adsorption technology. Nat. Protoc. 2006;1:2661. - PubMed
-
- Ambika S., Devasena M., Nambi I.M. Synthesis, characterization and performance of high energy ball milled meso-scale zero valent iron in Fenton reaction. J. Environ. Manage. 2016;181:847–855. - PubMed
-
- Bao S., Liu H., Liu Y., Yang W., Wang Y., Yu Y., Sun Y., Li K. Amino-functionalized graphene oxide-supported networked Pd–Ag nanowires as highly efficient catalyst for reducing Cr (VI) in industrial effluent by formic acid. Chemosphere. 2020 - PubMed
-
- Barrera-Díaz C.E., Lugo-Lugo V., Bilyeu B. A review of chemical, electrochemical and biological methods for aqueous Cr (VI) reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012;223:1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

